Formatting prepares a HDD for data storage, affecting data presentation, while partitioning divides it into sections for organization and access.
What is Formatting?
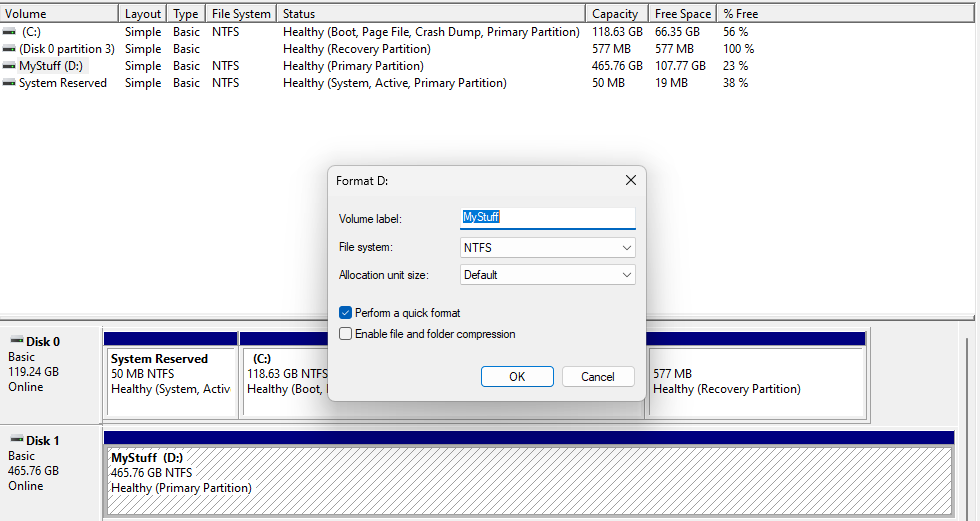
Formatting is the process of preparing a disk or storage device for data storage. It involves creating a file system, which determines how data is organized and accessed on the storage medium. Formatting can be thought of as creating a structure or layout on the disk that allows the operating system to read and write data.
Definition of Formatting
Formatting a HDD (Hard Disk Drive) is the process of preparing the storage medium for data storage and retrieval. It involves configuring the disk’s file system structure, which dictates how data is organized, stored, and accessed. During formatting, any existing data on the drive is usually erased, making space available for new information. This procedure can be quick or thorough, depending on the chosen format type, such as quick format or full format. Formatting is commonly used when setting up a new drive, resolving data corruption issues, or ensuring data privacy by securely erasing sensitive information. It is a critical step in maintaining data integrity and storage efficiency.
What is Partitioning?
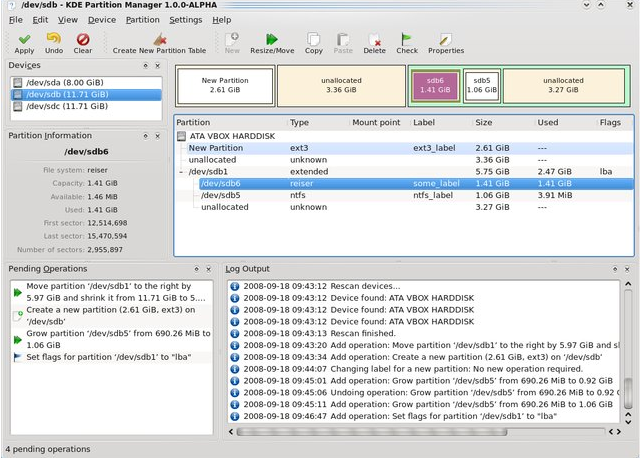
Partitioning, on the other hand, is the process of dividing a storage device into multiple logical sections, known as partitions. Each partition functions as a separate unit and can be treated as an independent storage space. Partitioning allows for better organization and management of files and can also enable the use of different operating systems on the same device.
Definition of Partitioning
Partitioning, defined as the process of dividing a storage device, such as a hard drive, into separate sections or partitions, plays a crucial role in optimizing storage space and improving system performance. Each partition functions as its own logical unit, with its own file system, allowing users to organize and manage data more efficiently.
The definition of partitioning involves creating boundaries within a storage device to establish separate areas for data management. Each partition is assigned a specific size and file system that determines how the data is stored and accessed. This enables users to allocate specific sections for different purposes, such as dedicating one partition to the operating system and another for personal files or applications.
Furthermore, partitioning enables users to set up different operating systems on a single device. By creating separate partitions, users can install multiple operating systems, such as Windows and Linux, which can be selected at startup. Partitioning is a fundamental concept in computer storage management, allowing users to effectively organize and utilize their storage space according to their specific needs.
Partitioning has been a common practice in computer storage management since the early days of computers. As technology advanced, the need for dividing storage devices into separate sections became more prominent, leading to the development of various partitioning techniques and software tools. The concept of partitioning has evolved alongside the advancements in storage technology, providing users with more flexibility and control over their data management.
Differences Between Formatting and Partitioning
When it comes to formatting and partitioning, understanding their differences is key. In this section, we’ll explore the nuances of these two processes and how they impact our data.
- Purpose: The purpose of formatting is to prepare the storage device for data storage, while partitioning is about dividing the device into separate sections for better organization and management.
- Functionality: Formatting establishes the file system and enables data reading and writing, while partitioning creates separate storage areas that can be utilized differently.
- Impact on Data: Formatting erases all existing data on the storage device, whereas partitioning does not delete data but allocates it to different sections.
- Compatibility: Different file systems can be used for formatting, providing compatibility with different operating systems, while partitioning creates separate sections that can be formatted with different file systems.
- Reversibility: Formatting can be reversed, but it will result in data loss, while partitioning can be modified or removed without data loss if done correctly.
1. Purpose
The purpose of formatting and partitioning are different when it comes to data storage and organization. Here is a breakdown of the purpose of each:
|
While formatting and partitioning are related and often done together, they serve different purposes. Formatting focuses on preparing the storage device for data storage, while partitioning focuses on dividing the storage into separate sections for different purposes. Understanding the purpose of each is important when setting up or managing your storage devices.
2. Functionality
| Functionality | Formatting | Partitioning |
|---|---|---|
| Changes the appearance and style of data | Yes (e.g., text, images, tables) | No |
| Splits a storage device into distinct sections | No | Yes |
| Can be applied to various elements like text, images, and tables | Yes | No |
| Primarily used for organizing and managing data on a storage device | Yes | Yes |
| Affects the visual presentation of data | Yes | No |
| Affects how data is stored and accessed | Yes | Yes |
| Does not alter the actual data | No | Yes |
| Does not affect the visual appearance of data | No | Yes |
| Can be easily reversed or changed without impacting the data | Yes | No |
| Permanent change that cannot be reversed without data loss | No | Yes |
Fact: Partitioning a storage device can improve the overall performance and efficiency of data storage and retrieval processes.
3. Impact on Data
When it comes to formatting and partitioning, both have an impact on data. Let’s take a closer look at this aspect:
| Formatting | Partitioning |
| Formatting involves the organization and structure of data within a storage device or file system. | Partitioning refers to the division of a storage device into separate sections called partitions. |
| Formatting can affect data by erasing or changing the file system, potentially leading to data loss. | Partitioning impacts data by creating logical sections that can be managed independently. |
| Formatted data is typically compatible with different operating systems and can be accessed across platforms. | Partitioned data can be specifically formatted according to the file system requirements of a particular operating system. |
| Formatting is reversible, allowing data to be restored if a backup or recovery method is employed. | Partitioning itself does not have a direct impact on the ability to reverse formatting. |
The impact on data is an important consideration when deciding between formatting and partitioning. Understanding how each process affects data can help in making informed decisions about storage management.
4. Compatibility
| Compatibility Aspect | Formatting | Partitioning |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility with different operating systems | When discussing the differences between formatting and partitioning, it is important to consider compatibility with different operating systems. Formatting can be specific to certain operating systems and file systems, which may cause compatibility issues when transferring data between different systems. On the other hand, partitioning allows for better compatibility between different operating systems as partitions can be created in formats that are widely supported. | Partitioning offers better compatibility with different operating systems compared to formatting. This is because partitions can be created to be compatible with various operating systems, resulting in smoother data transfer between different systems. |
| Compatibility with different devices | Another aspect to consider is compatibility with different devices. Formatting may restrict the use of storage devices to a specific device type, limiting compatibility with other devices. For example, a device formatted for Mac may not be compatible with Windows. Conversely, partitioning allows for better compatibility across different devices as partitions can be created to be compatible with various device types. | Partitioning provides better compatibility across different devices compared to formatting. By creating partitions that are compatible with various device types, the limitations on device compatibility are significantly reduced. |
| Compatibility with existing data | When it comes to compatibility with existing data, formatting typically erases all data on a storage device, making it incompatible with existing data unless it is backed up or transferred elsewhere. On the other hand, partitioning allows for compatibility with existing data. By creating separate storage areas, partitioning ensures that the data on other partitions remains unaffected. | In terms of compatibility with existing data, partitioning is the preferred option. With partitioning, separate storage areas are created, allowing for compatibility with existing data without affecting it. |
When making a choice between formatting and partitioning, it is crucial to consider the compatibility aspect. If you require compatibility across different operating systems and devices or need to preserve existing data, partitioning is a better option. On the other hand, if you are using a specific operating system and have no concerns about compatibility, formatting may be sufficient.
5. Reversibility
- Reversibility is an important feature that allows one to easily undo or revert any changes made during formatting or partitioning process.
- During the process of formatting, reversibility becomes essential as it allows users to remove any formatting and restore the storage device back to its original state.
- It is worth noting that formatting a storage device is an irreversible action which erases all existing data and prepares the device for future use.
- Alternatively, partitioning involves dividing a storage device into separate sections or partitions, each with its own dedicated file system.
- Partitioning can be made reversible in the sense that the created partitions can be deleted or merged, which then allows the storage device to be restored to its original state prior to the partitioning process.
Pro-tip: It is highly recommended to always back up your important data before carrying out any formatting or partitioning activities to prevent any irreversible data loss.
Common Misconceptions
In the world of technology, there are common misconceptions surrounding the difference between formatting and partitioning. Let’s dive in and debunk these misunderstandings. We’ll uncover whether formatting erases partitions, how partitioning can affect formatting, and whether these two processes actually serve the same purpose. Get ready to unravel the truth behind formatting and partitioning in this tech-savvy exploration.
1. Formatting Erases Partitions
- Formatting is the process of preparing a storage medium, such as a hard drive or a USB drive, to store and organize data by creating a file system. It involves setting up the necessary structures and metadata to enable the storage and retrieval of files.
- Formatting typically erases all data on the storage medium, including partitions. When you format a storage device, it wipes out the existing file system and replaces it with a new one, effectively erasing all partitions and their associated data.
- Formatting can be done in different file system formats, such as FAT32, NTFS, or exFAT, depending on the intended use and compatibility with different operating systems.
- It is important to note that formatting erases only the data and file system structures, not the physical storage itself. The actual bits of data are not overwritten during the formatting process; they become inaccessible and can potentially be recovered using specialized tools until new data is written over them.
- If you want to preserve the partitions and their data, it is essential to back up the data before formatting the storage device.
2. Partitioning Affects Formatting
Partitioning and formatting are interdependent processes that directly impact each other. The process of partitioning involves dividing a hard drive into separate sections or partitions, while formatting prepares a partition or storage device for data storage by creating a file system.
When a hard drive is partitioned, each partition is assigned a specific file system such as NTFS or FAT32. This assignment determines how the data is organized and stored on that partition. Therefore, the choice of partitioning directly affects the formatting process, as the file system needs to be compatible with the partition.
The size and allocation of partitions during partitioning can also impact the formatting process. If a partition is too small, there may not be enough space to properly format it. Conversely, if a partition is too large, it could result in wasted space or inefficient resource usage.
In addition, partitioning affects the formatting process in terms of data organization and accessibility. Different partitions can have varying levels of access restrictions or encryption settings, which can influence how the formatting process is carried out.
Over the years, partitioning and formatting have been essential steps in creating a functional storage system for computers. In the past, these processes required manual execution through complex command-line interfaces. However, with the advent of graphical user interfaces and user-friendly operating systems, partitioning and formatting have become much simpler. Nowadays, users can easily manage their storage devices, create multiple partitions, and format them according to their specific needs, all with just a few clicks using intuitive tools provided by operating systems.
The continuous advancements in storage technology and operating systems further enhance the efficiency and flexibility of partitioning and formatting processes. Consequently, users can optimize their storage devices and make the most out of them with ease.
3. Formatting and Partitioning Serve the Same Purpose
| Facts | Formatting | Partitioning |
| 1 | Definition | Definition |
| 2 | Process of preparing a storage device for data storage | Process of dividing a storage device into separate sections |
| 3 | Organizes the file system and structures data storage | Divides a storage device into multiple logical drives or partitions |
| 4 | Facilitates access, retrieval, and organization of data | Allows for different file systems and storage configurations |
| 5 | Enables the installation of an operating system and software | Enables data organization, backup, and security measures |
When it comes to the purpose, formatting and partitioning do not serve the same purpose. Instead, they serve different functions. Formatting focuses on preparing a storage device for data storage, organizing the file system, and facilitating access to data. On the other hand, partitioning involves dividing a storage device into separate sections, allowing for different file systems and storage configurations, and enabling data organization, backup, and security measures.
While formatting primarily focuses on the structure of the storage device, partitioning focuses on the logical organization of data within the storage device. Both processes are important and complement each other in ensuring efficient data storage and management.
To make the most out of your storage device, it is essential to understand the purpose of formatting and partitioning and utilize them according to your specific needs. Format your storage device to prepare it for data storage, and then partition it to organize and optimize data access and management.
Remember, formatting and partitioning are distinct processes and should not be mistaken as serving the same purpose. Each plays a crucial role in creating an efficient and effective storage solution.
So, when setting up or managing your storage device, be sure to consider both formatting and partitioning to optimize your data storage.
Some Facts About What’s the Difference Between Formatting And Partitioning:
- ✅ Partitioning is the process of dividing a drive into logical units of space, while formatting is the act of creating a file system on a volume.
- ✅ Multiple partitions can be created on a single drive, with different sizes and file systems, while formatting determines which file system will be on each partition.
- ✅ The size of a partition is determined during partitioning, and the file system will fill the entire partition when it is created.
- ✅ Different file systems cannot be placed on the same partition.
- ✅ Resizing a partition or file system requires expanding or shrinking one before the other, and some partitioning tools may automatically resize them without informing the user explicitly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between formatting and partitioning a hard drive?
Partitioning is the process of dividing a hard drive into logical units of space, while formatting is the act of creating a file system on a partition. Partitioning determines how much space will be allocated to each part of the drive, while formatting prepares the partition to store and retrieve data.
How does partitioning and formatting affect disk space?
Partitioning determines the size of each partition, and formatting fills up the entire partition with a file system. Different file systems cannot be placed on the same partition. If a partition is not fully filled with a file system, it may be because the partition was expanded or the file system was shrunk after initial creation.
Can I resize partitions and file systems after they are created?
Yes, it is possible to resize partitions and file systems. However, resizing either of them requires expanding or shrinking one before the other. Some partitioning tools may automatically resize the partition and file system layers without explicitly informing the user.
Do operating systems automatically partition and format the hard drive?
Yes, most operating systems automatically partition and format the hard drive during installation. This is done to prepare the partitions to hold files and applications necessary for the operating system to function.
What is the purpose of partitioning a hard drive during computer upgrades?
Partitioning a hard drive during computer upgrades allows for better organization and allocation of disk space. It enables the user to logically divide their hard drive into smaller sections, making it easier to manage files and applications.
Can I partition and format a brand new computer with no operating system?
Yes, it is possible to partition and format a brand new computer with no operating system. This process is necessary before installing an operating system, as it prepares the hard drive to hold the necessary files and applications.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Michael Schwarzenberger from Pixabay
Image 1 By – differencedigest
Image 2 By – KDE Partition Manager authors, GPL <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>, via Wikimedia Commons









