Ammonium nitrate is a highly soluble compound that provides a readily available source of nitrogen for plants. Ammonium sulfate contains both nitrogen and sulfur nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
TL;DR Ammonium nitrate Vs. Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium nitrate has a high nitrogen content (33-34%) and delivers quick-release nitrogen to promote rapid growth. However, due to its potential for misuse in explosives, it is heavily regulated and restricted in many countries. Ammonium sulfate has a lower nitrogen content (21%) compared to ammonium nitrate but offers the advantage of slow-release nitrogen, promoting consistent nutrition over an extended period. Additionally, the presence of sulfur makes it especially beneficial for crops with higher sulfur requirements.
What is ammonium nitrate?
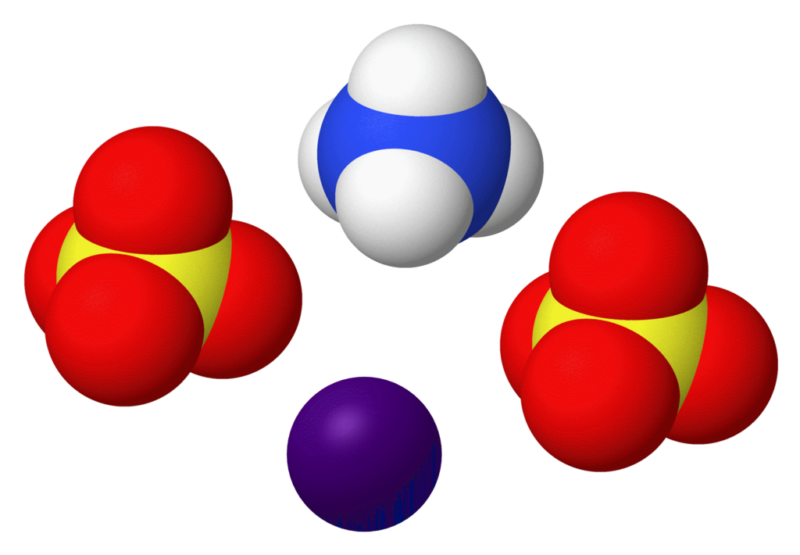
Ammonium nitrate, chemical formula NH4NO3, is a crystalline salt that consists of ammonium ions (NH4+) and nitrate ions (NO3-). It is widely used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. The compound itself is highly soluble in water, making it easily absorbed by plant roots.
One notable characteristic of ammonium nitrate is its ability to release nitrogen quickly upon contact with moisture. This fast-release property makes it an excellent choice for crops requiring an immediate nutrient boost. Additionally, the nitrogen released from this compound promotes vigorous growth and enhances the overall yield.
However, while ammonium nitrate provides rapid nitrogen availability to plants, it also has some downsides. When exposed to high temperatures or open flames, it can undergo decomposition reactions that generate oxygen gas and heat – potentially leading to combustion if not properly handled. Due to these safety concerns, regulations on the storage and handling of ammonium nitrate are strictly enforced.
What is ammonium sulfate?
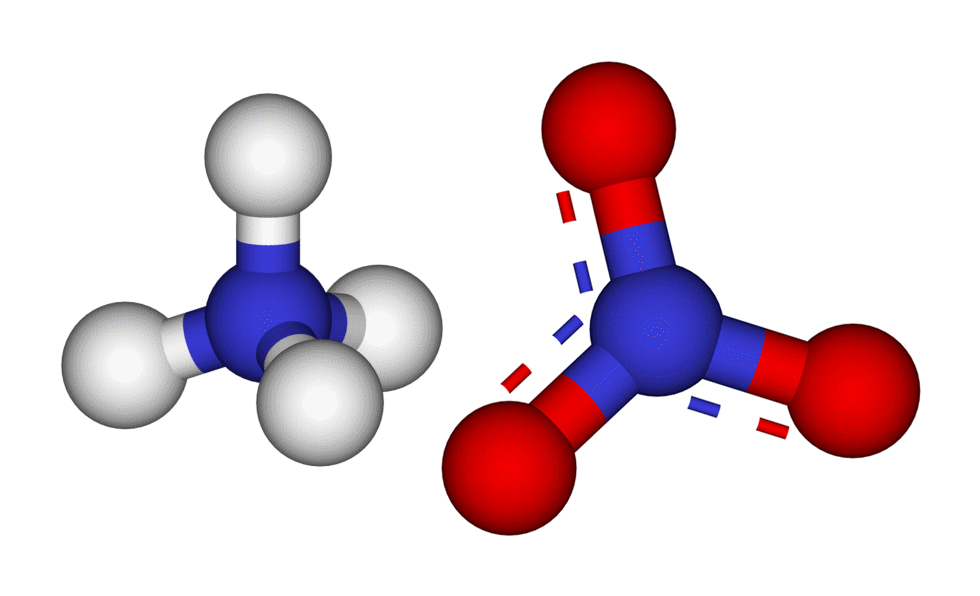
What is ammonium sulfate? It is a chemical compound that consists of two main components: ammonium ions (NH4+) and sulfate ions (SO4^2-). This white, crystalline substance has a molecular formula of (NH4)2SO4. Ammonium sulfate is commonly used in agriculture as a fertilizer because it provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
One key characteristic of ammonium sulfate is its solubility in water. Unlike some other fertilizers, it readily dissolves in water, allowing plants to efficiently absorb the nutrients it contains. This makes it an effective choice for both dry and liquid applications.
Ammonium sulfate plays a crucial role in promoting healthy plant growth and finding practical applications beyond just agriculture. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a valuable compound across different sectors.
Ammonium nitrate Vs. Ammonium sulfate – Key differences
| Ammonium Nitrate | Ammonium Sulfate | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | NH₄NO₃ | (NH₄)₂SO₄ |
| Composition | Nitrogen, Ammonium, and Nitrate ions | Nitrogen, Ammonium, and Sulfate ions |
| Appearance | White solid granules or prills | White crystalline solid or granules |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water | Highly soluble in water |
| Nitrogen Content | Contains high nitrogen content (33-34%) | Contains moderate nitrogen content (20-21%) |
| Sulfur Content | Does not contain sulfur | Contains sulfur (24%) |
| pH Value | Neutral to slightly acidic | Slightly acidic to neutral |
| Common Uses | Fertilizer, explosive, and blasting agent | Fertilizer, soil amendment, and pH adjuster |
| Stability | Relatively stable under normal conditions | Relatively stable under normal conditions |
| Hygroscopicity | Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from air) | Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from air) |
| Agricultural Concerns | Can contribute to groundwater contamination | Can contribute to soil acidification |
Uses of ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate?
Ammonium Nitrate
- Fertilizer: Ammonium nitrate is commonly used as a nitrogen-based fertilizer in agriculture. It provides a readily available source of nitrogen for plants, promoting their growth and development.
- Explosives: Due to its high nitrogen content and ability to support rapid combustion, ammonium nitrate is also used as an ingredient in explosives and blasting agents. However, its use in this context is highly regulated due to safety concerns.
- Cold packs: Ammonium nitrate can be found in some cold packs or instant cold compresses. When mixed with water, it absorbs heat from the surroundings, causing a cooling effect.
- Oxidizer: Ammonium nitrate is utilized as an oxidizer in certain applications, such as solid rocket propellants and pyrotechnics.
Ammonium Sulfate
- Fertilizer: Ammonium sulfate is widely used as a nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer in agriculture. It provides a source of both nutrients, supporting plant growth and enhancing crop yields. It is particularly beneficial for crops that require or benefit from additional sulfur.
- Soil Amendment: Ammonium sulfate can be applied to soil as an amendment to help adjust pH levels. It can help lower the pH of alkaline soils, making them more suitable for certain plants that thrive in acidic conditions.
- Industrial applications: Ammonium sulfate finds application in various industrial processes. It is used in the production of fire extinguisher powder, as a flame retardant in textiles, as a food additive to regulate acidity, and in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals and dyes.
- Laboratory reagent: Ammonium sulfate is utilized as a reagent in laboratory settings for various purposes, such as protein purification, DNA precipitation, and as a stabilizing agent for some analytical methods.
It’s important to note that the specific uses and applications of ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate may vary depending on local regulations, safety considerations, and specific industry requirements.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Hoa112008, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 1 By – Claudio Pistilli, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 2 By – Jynto and Ben Mills, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons