Hyperpigmentation and melasma are two common skin conditions that can cause discoloration on the face. While they may seem similar, it is important to understand their differences in order to properly treat them. Hyperpigmentation is caused by an excess of melanin whereas melasma is triggered by hormonal fluctuations or sun exposure. Treatment for both include topical creams, laser treatments or chemical peels depending on the severity of your case. With proper skincare and precautions, you should be able to keep hyperpigmentation and melasma at bay
What is hyperpigmentation?
(Photo By Kylie Aquino on Flickr)
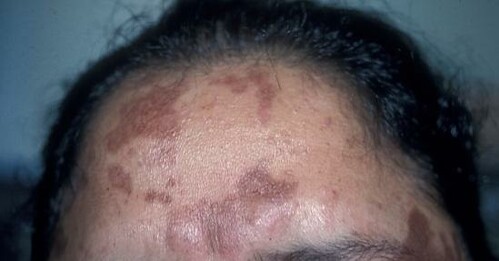
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition in which patches of skin become darker than the surrounding skin. This happens when the body produces excess melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, including:
- Age spots: Also known as liver spots, these are flat, brown spots that appear on areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms.
- Melasma: This type of hyperpigmentation is characterized by brown or gray-brown patches that typically appear on the face, particularly on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and upper lip. Melasma is often associated with hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs when the skin produces excess melanin in response to inflammation or injury, such as acne, eczema, or a cut or scrape.
Hyperpigmentation is generally a harmless condition and does not require medical treatment. However, many people choose to treat it for cosmetic reasons. Treatment options may include topical creams or gels that contain hydroquinone, kojic acid, or other skin lightening agents, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best treatment approach for your specific type and severity of hyperpigmentation.
What is melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition that causes patches of dark, discolored skin to develop on the face. The patches can range in color from light brown to black and are often symmetrical, meaning they appear on both sides of the face. Melasma typically occurs in women, particularly during pregnancy or when taking certain types of birth control pills. However, men can also develop melasma. The exact cause of melasma is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes. Sun exposure can also make melasma worse. There is no cure for melasma, but treatments are available to help fade the dark patches.
Causes of hyperpigmentation and melasma
There are many different possible causes of hyperpigmentation and melasma. Some common potential causes include sun exposure, hormonal changes, certain medications, and skin injuries.
Sun exposure is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation and melasma. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can damage the skin and trigger the production of excess melanin, which can lead to darkening of the skin.
Hormonal changes can also cause hyperpigmentation and melasma. For example, during pregnancy or puberty, levels of certain hormones (such as estrogen) may increase, which can stimulate melanin production and result in darkening of the skin. Certain medications (such as birth control pills) can also cause hormonal changes that may lead to hyperpigmentation or melasma.
Skin injuries (such as cuts, scrapes, or burns) can also cause hyperpigmentation by triggering an overproduction of melanin in the affected area. In some cases, hyperpigmentation may also be caused by an underlying medical condition such as Addison’s disease or Cushing’s syndrome.
Treatment options for hyperpigmentation and melasma
(Photo By Kylie Aquino on Flickr)

There are a few different ways to treat hyperpigmentation and melasma. The first option is to use a lightening cream or serum. There are many products on the market that can help to lighten the skin. These products usually contain ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or vitamin C. Another option is to use a laser treatment. This can be done in a dermatologist’s office and can help to break up the pigmentation in the skin. IPL (intense pulsed light) treatments are also an option for treating hyperpigmentation and melasma. These treatments can be done at home or in a dermatologist’s office.
Prevention of hyperpigmentation and melasma
Hyperpigmentation is the result of an overproduction of melanin in the skin. This can be caused by things like sun damage, inflammation, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that is often triggered by hormones, pregnancy, or birth control pills. It tends to be more prevalent in women than men.
There are a few different ways to prevent hyperpigmentation and melasma. First, it’s important to protect your skin from the sun with sunscreen and clothing. If you’re using any medications that can cause hyperpigmentation, talk to your doctor about alternative options. Finally, try to avoid any triggers that may cause your melasma to flare up (such as pregnancy or taking birth control pills).
How can you tell melasma from hyperpigmentation?
There are a few key ways to distinguish melasma from hyperpigmentation. First, melasma typically appears as symmetrical dark patches on the face, while hyperpigmentation can appear anywhere on the body and is often more irregular in shape. Second, melasma is more likely to be triggered or worsened by sun exposure, while hyperpigmentation is not as closely linked to sun exposure. Finally, melasma typically affects women of childbearing age, while hyperpigmentation can affect anyone. If you’re unsure whether you have melasma or hyperpigmentation, it’s best to consult with a dermatologist.
How do you know if you have melasma?
If you have melasma, you will notice patches of dark, discolored skin on your face. These patches are usually symmetrical, meaning they appear on both sides of your face. They may also appear on other parts of your body that are exposed to the sun, such as your neck, chest, and hands. Melasma is often mistaken for hyperpigmentation, but there are a few key differences. For one, melasma usually occurs in women who are pregnant or taking birth control pills. Hyperpigmentation can occur in anyone, regardless of gender or hormone levels. Additionally, melasma typically appears as large patches of darker skin, while hyperpigmentation tends to be more scattered and less noticeable. If you’re not sure whether you have melasma or hyperpigmentation, consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis.
Can melasma fade away?
Yes, melasma can fade away on its own over time, particularly if it is related to hormonal changes such as those that occur during pregnancy. However, in many cases, melasma may persist or even worsen over time.
There are several treatment options available for melasma that can help to lighten the skin and reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. These may include topical treatments such as hydroquinone, tretinoin, or azelaic acid, as well as procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy. It is important to work with a dermatologist to determine the best treatment approach for your specific type and severity of melasma.
It is also important to protect your skin from further sun damage by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure, particularly during the middle of the day when the sun’s rays are strongest. Sun exposure can worsen melasma and make it more difficult to treat.
Can hyperpigmentation be cured?
Hyperpigmentation can be treated, but it may not necessarily be “cured” completely. The goal of treatment is typically to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and even out skin tone.
Treatment options for hyperpigmentation may include topical creams or gels that contain skin-lightening agents such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, or azelaic acid. These products work by inhibiting the production of melanin in the skin. Other treatment options may include chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy, which can help to remove the top layer of skin and promote the growth of new, unblemished skin cells.
It is important to note that hyperpigmentation may recur after treatment, particularly if the underlying cause is not addressed. For example, if hyperpigmentation is caused by sun damage, it may return if the individual continues to spend time in the sun without adequate protection. It is important to work with a dermatologist to identify the underlying cause of hyperpigmentation and develop an appropriate treatment plan that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying cause.
Featured Image By – Kylie Aquino on Flickr