Type one is an autoimmune disorder that affects insulin production, while type two is a metabolic disorder caused by lifestyle choices like poor diet and lack of exercise. Both types require monitoring blood sugar levels as well as taking medications or making lifestyle changes to manage symptoms. It’s important for those with either form of diabetes to work closely with their healthcare provider in order to stay healthy and manage their condition effectively.
What is diabetes?
There are two main types of diabetes, type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, adolescents or young adults. It occurs when the body can no longer produce insulin, which is necessary to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of the disease and typically develops in adulthood. It occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use it effectively.
Type one and type two diabetes – Key differences
Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a form of diabetes that usually develops in childhood or adolescence. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to control blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes, previously known as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, is a form of diabetes that usually develops in adulthood. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. As a result, blood sugar levels become too high.
The symptoms of type one and type two diabetes
The symptoms of type one and type two diabetes are very similar. They both include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and weight loss. The main difference between the two is that type one diabetes is characterized by ketoacidosis, while type two diabetes is not. Ketoacidosis is a condition in which the body produces too much ketone, an acidic compound that can build up in the blood and cause serious health problems.
The treatment of type one and type two diabetes
(Image by Photo Mix from Pixabay )
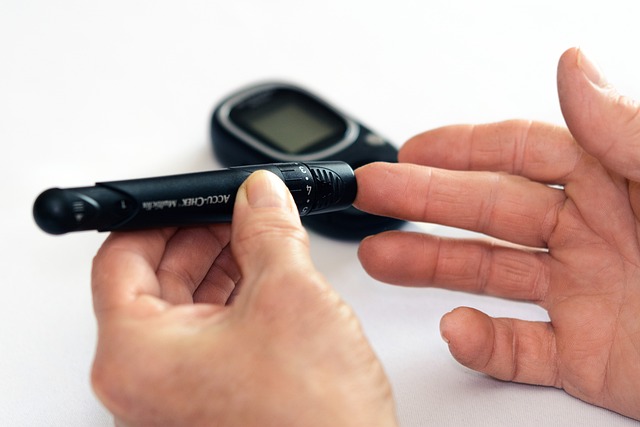
While there is no cure for either type of diabetes, both can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication. For people with type one diabetes, this includes taking daily insulin injections and monitoring blood sugar levels closely. For people with type two diabetes, treatment typically involves a combination of diet, exercise, and oral medications or insulin injections.
Is type 1 or type 2 diabetes more serious?
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on the individual case. Type 1 diabetes is typically more serious in terms of the potential complications and health risks associated with it, but this is not always the case. Type 2 diabetes can also be very serious, particularly if it is not well-controlled. In general, type 1 diabetes is considered to be more serious because it often requires insulin therapy and can lead to complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetic neuropathy. However, both types of diabetes can be extremely serious if they are not managed properly.
How are type 1 and type 2 diabetes treated differently?
Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin therapy, while type 2 diabetes may be managed with diet and lifestyle changes, oral medication, or insulin therapy. Insulin therapy for type 1 diabetes may involve multiple daily injections of insulin or the use of an insulin pump.
Can type 2 diabetes go away?
There is no cure for type 1 diabetes, but it can go into remission. This means that, for a period of time, you may be able to manage your diabetes without insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes is not currently curable, but it is possible to put the disease into remission. This means making lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise) that can lead to sustained weight loss.
Can type 2 diabetes turn into type 1?
There is no definitive answer to this question as everyone is different. Type 2 diabetes can develop into type 1 diabetes in some people, while others may only experience milder symptoms of type 2 diabetes. It is important to work with a healthcare team to monitor your diabetes and make necessary lifestyle changes to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
| Warning Signs of Type1 Diabetes | Things That Can Trigger Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Increased thirst | A sedentary lifestyle |
| Frequent urination | Poor diet |
| Extreme hunger | A family history of diabetes |
| Weight loss | Increasing age |
| Fatigue | High blood pressure |
| Irritability | High cholesterol |
Can you suddenly get type 1 diabetes?
No, you cannot suddenly get type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is not something that just happens; it is an autoimmune disease that someone is born with or that develops over time. However, if you have a family member with type 1 diabetes, you may be at increased risk for developing the disease yourself.
Can stress trigger diabetes?
Stress has long been known to wreak havoc on our health, and new research suggests that it may also play a role in the development of type 1 diabetes. While the exact mechanism is still not fully understood, scientists believe that stress may trigger the body to attack its own cells, leading to the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells. This process is thought to be similar to what happens in other autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and celiac disease.
While more research is needed to confirm this link, it’s yet another reminder of the importance of managing stress levels and taking care of our mental health. If you’re struggling with stress, talk to your doctor or a mental health professional about ways to manage it.
What 10 foods should diabetics avoid?
1. Sugary foods: Diabetics should avoid sugary foods like candy, cookies, cake, and soda. These foods can cause blood sugar spikes, which can be dangerous for diabetics.
2. Processed carbohydrates: Diabetics should avoid processed carbs like white bread, pasta, and rice. These carbs are quickly broken down into sugar in the body, which can cause blood sugar spikes.
3. Trans fats: Diabetics should avoid trans fats, which are found in many processed foods. Trans fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
4. Saturated fats: Diabetics should also avoid saturated fats, which are found in animal products like meat and dairy. Saturated fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
5. High-sodium foods: Diabetics should avoid high-sodium foods like processed meats, canned soups, and fast food. High sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, which is a risk factor for heart disease.
6. Alcohol: Diabetics should limit their alcohol intake as it can cause blood sugar spikes. Alcohol can also interact with diabetes medications and make them less effective.
7. Caffeine: Diabetics should limit their caffeine intake as it can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Caffeine can also interact with diabetes medications and make them less
What foods can diabetics eat freely?
There are no foods that diabetics can eat freely. All food choices must be made with care and consideration for blood sugar levels. That said, there are some general guidelines that can help diabetics make healthier choices.
In general, complex carbohydrates like whole grains and legumes are better choices than simple sugars. These complex carbs take longer to break down, which helps keep blood sugar levels more stable. Fiber is also an important nutrient for diabetics, as it helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
Diabetics should also focus on getting plenty of healthy fats and proteins in their diet. Healthy fats help promote satiety and stabilizing blood sugar levels, while proteins provide essential nutrients and help repair tissues throughout the body.
Featured Image by Towfiqu barbhuiya on Unsplash