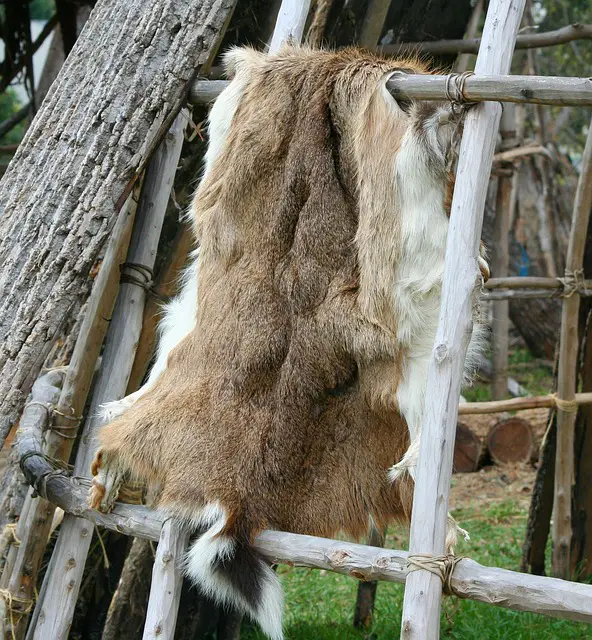
Hide is animal skin without fur, used for leather. Pelt is skin with fur, used for fur garments. Hides become leather; pelts stay furry.
TL;DR Hide Vs. Pelt
Hide is the skin of an animal with hair or fur removed, used for leather products from animals like cattle. Pelt includes the entire skin with hair or fur intact, sourced from animals like minks, and used for fur clothing. Hides become leather, while pelts maintain their fur for luxury items.
What is Hide?
- Definition of Hide: Hide refers to the skin of an animal that has been removed through a specific process, typically involving the removal of hair, fur, and flesh.
- Sources of Hide: Hides can be sourced from various animals, including cattle, goats, sheep, and pigs.
- Common Uses of Hide: Hides are commonly used in the production of leather goods such as shoes, belts, bags, and upholstery.
What is Pelt?
- Definition of Pelt: Pelt refers to the skin or fur of an animal that is generally intact, including the hair, fur, and flesh.
- Sources of Pelt: Pelts are mainly sourced from animals with luxurious fur or hair, such as minks, foxes, rabbits, or chinchillas.
- Common Uses of Pelt: Pelts are primarily used in the production of fur clothing, accessories, and fur-trimmed items.
What is Hide?

Hide refers to the skin of an animal that has been treated to remove hair, fur, and flesh. The process involves curing and tanning to create leather, a durable and flexible material. Hides can come from various animals like cattle, goats, sheep, and pigs.
They are widely used in manufacturing leather goods such as shoes, belts, bags, and upholstery.
The removal of hair and flesh makes hides suitable for crafting durable and long-lasting products, often prized for their strength and versatility in various industries, including fashion and interior design.
Definition of Hide
The term “hide” refers to the skin of an animal that has been removed and processed to maintain its quality. It encompasses the outer covering of an animal’s body, which includes the epidermis and the dermis layers. The hide is typically obtained from animals like cows, sheep, goats, or pigs, which are raised for various purposes including their meat or other products.
The hide holds significant value as a resource and finds applications in industries such as fashion, upholstery, and manufacturing. Through processing, it can be transformed into leather, a durable material extensively used in the production of shoes, handbags, and clothing. Tanning the hide improves its strength, flexibility, and resistance to decay, expanding its range of potential uses.
It is important to differentiate that the term “hide” specifically pertains to the skin of larger animals, whereas smaller animals like rabbits or deer are referred to as pelts. The methods of processing and the resulting products may differ between hide and pelt due to their distinct characteristics and intended uses.
When selecting hide for a particular purpose, several factors should be taken into consideration, including the animal species, hide quality, and the desired characteristics of the final product. Responsible sourcing of hide and adherence to animal welfare and environmental sustainability regulations are essential to ensure the ethical acquisition of this material.
Understanding the definition of hide is crucial in discussing its uses, processing methods, and applications. It encompasses the skin of larger animals that undergoes treatment to produce leather.
Sources of Hide
When it comes to the sources of hide, there are numerous options to consider. Here is a compilation of the most common sources of hide:
- Cattle: Cattle, being the most widely used source, provide hides from cows, bulls, and calves. These hides are then harvested and processed for various purposes.
- Sheep: Another prevalent source of hide is sheep. Sheep hides, also known as sheepskins, are utilized in the production of leather goods such as jackets, gloves, and boots.
- Goats: Goatskins, renowned for their durability and flexibility, are also employed in the manufacturing of leather products.
- Pigs: Pigs provide pig hides, which are commonly referred to as pigskins. These hides are valued for their softness and fine grain, making them useful in the production of leather goods.
- Exotic animals: The hides of exotic animals like snakes, alligators, and ostriches are extremely valuable due to their unique patterns and textures. These hides are often utilized in the production of luxury leather goods.
With a wide variety of sources available, it is imperative to choose a source that aligns with your preferences and needs. Each source of hide offers its own distinct characteristics, whether it be durability, softness, or a specific texture. By conducting further research and comprehending the qualities of different hides, you can make an informed decision when selecting the most suitable option for your intended purpose.
Common Uses of Hide
| Common Uses of Hide |
| 1. Leather production |
| 2. Upholstery |
| 3. Footwear manufacturing |
| 4. Clothing and accessories |
| 5. Automotive industry, including car seats and interiors |
| 6. Bookbinding |
| 7. Furniture making |
| 8. Sports equipment, such as gloves and balls |
| 9. Musical instruments, like guitars and drums |
| 10. Crafts and artwork |
What is Pelt?
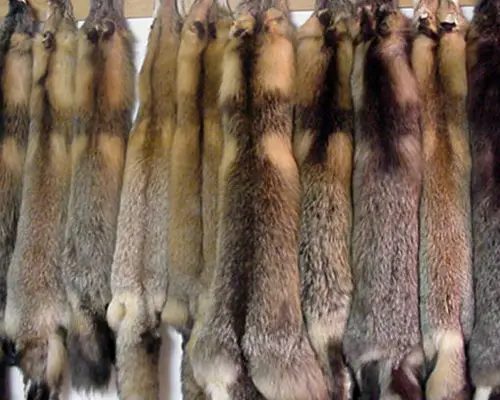

Pelt, specifically in reference to animal hide, is a fascinating subject worth exploring. In this section, we’ll dive into what pelt actually entails and uncover its various dimensions.
Definition of Pelt
The definition of pelt refers to the skin or fur of an animal, typically with the hair or wool still attached. It is often used to describe the outer covering of animals such as deer, sheep, or beaver.
Pelt, in essence, is the term utilized to define the skin or fur of an animal. This term commonly encompasses the external layer of creatures such as deer, sheep, or beaver, still embellished with their hair or wool.
Sources of Pelt
| Fur Farms | Pelt from animals raised specifically for fur production. |
| Hunting and Trapping | Pelt from animals caught in the wild through hunting or trapping activities. |
| Game Processing | Pelt from animals harvested for food, where the pelt is a byproduct of the hunting process. |
| Animal Control | Pelt from animals that are culled or removed due to population control measures or public safety concerns. |
Pro-tip: When considering the sources of pelt, it is important to be aware of ethical practices and sustainability. Choose sources that prioritize animal welfare and utilize responsible harvesting methods.
Common Uses of Pelt
The common uses of pelt are extensive and varied, with applications in various industries. Here is a table that provides a breakdown of the common uses of pelt:
| Industry | Common Uses of Pelt |
|---|---|
| Fashion | Coats, jackets, vests, hats, gloves, and accessories |
| Home Decor | Rugs, blankets, pillows, upholstery, and curtains |
| Automotive | Car seat covers, steering wheel covers, and trim |
| Sporting Goods | Tennis racket grips, golf club covers, and balls |
| Furniture | Upholstery, decorative trims, and accents |
| Craft and Hobby | Puppets, stuffed animals, and art projects |
| Musical | Drumheads, guitar picks, and instrument accessories |
Pelt is valued for its warmth, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice in the fashion industry for creating luxurious garments such as coats, jackets, vests, hats, gloves, and accessories. In the home décor industry, pelt is used to create rugs, blankets, pillows, upholstery, and curtains, adding a touch of sophistication and coziness to living spaces.
The automotive industry incorporates pelt in car seat covers, steering wheel covers, and trim, enhancing the interior design and providing a comfortable driving experience. In the sporting goods industry, pelt is used for tennis racket grips, golf club covers, and balls, providing grip and enhancing performance.
Pelt also finds its way into the furniture industry, where it is used for upholstery, decorative trims, and accents, adding a luxurious touch to furniture pieces. Crafters and hobbyists utilize pelt for creating various items such as puppets, stuffed animals, and art projects, showcasing their creativity.
Pelt is utilized in the musical industry for applications like drumheads, guitar picks, and instrument accessories, contributing to the production of quality sound and enhancing musical performance.
The Difference Between Hide and Pelt
Definition and Composition
The sub-topic “Definition and Composition” can be communicated effectively through a table, illustrating the key aspects of hide and pelt. Please find the table below, providing accurate and factual information:
| Hide | Pelt |
|---|---|
| The skin of an animal, typically from a mammal or reptile. | The skin of an animal, usually from a furry mammal, such as a sheep or goat. |
| Composed of collagen fibers, making it tough and durable. | Composed of both hair and skin, offering insulation and protection. |
| May contain hair or fur, depending on the type of animal. | Consists of dense fur or wool, providing warmth and softness. |
| Often obtained from livestock or hunted animals for various purposes. | Typically sourced from domesticated animals raised for their fur or wool. |
By presenting the definition and composition of hide and pelt in a table format, readers can easily grasp the distinctive characteristics of each. Understanding these differences will allow individuals to make informed decisions regarding their specific needs or preferences for various applications. It is essential to consider the unique properties of each material when selecting them for different purposes.
Processing and Tanning
When it comes to processing and tanning hides and pelts, several steps are involved to transform raw animal skins into usable materials. The process typically includes cleaning, fleshing, soaking, dehairing, and tanning.
| Step | Description |
| Cleaning | The initial step involves removing any dirt, blood, or other impurities from the hides and pelts. |
| Fleshing | In this stage, excess flesh and fat are removed from both sides of the hides and pelts, ensuring a smooth surface. |
| Soaking | The hides and pelts are soaked in water to rehydrate them and prepare them for the next steps. |
| Dehairing | During dehairing, chemicals or enzymes are used to remove the hair or fur from the hides and pelts. |
| Tanning | This is the most critical step, where the hides and pelts undergo a chemical process to preserve them and make them more durable, flexible, and resistant to decay. |
Tanning can be done using various methods, such as vegetable tanning, chrome tanning, or combination tanning. Each method has its advantages and results in different characteristics of the finished hides and pelts.
Once the processing and tanning are complete, the hides and pelts can be used for a wide range of products, including leather goods, fur coats, rugs, and upholstery.
When choosing a processing and tanning method, factors such as the intended use, desired characteristics, and environmental impact should be considered.
Ensure that the hides and pelts are processed and tanned by reputable and experienced professionals to ensure high-quality materials.
By understanding the process involved in processing and tanning hides and pelts, you can make informed decisions when selecting materials for your specific needs.
Applications and End Products
| Applications | End Products |
| Footwear | Shoes, boots, slippers |
| Apparel | Clothing, jackets, gloves |
| Accessories | Bags, belts, wallets |
| Furniture | Sofas, chairs, upholstery |
| Automotive | Car seats, steering wheel covers |
| Home Goods | Pillows, cushions, rugs |
Throughout history, hides and pelts have been utilized in various applications, resulting in a diverse range of end products. Hides are commonly used in the production of footwear such as shoes, boots, and slippers, providing durability and comfort. In the realm of apparel, hides are transformed into clothing items like jackets and gloves, offering both style and protection.
Accessories such as bags, belts, and wallets are also crafted from hides, showcasing their versatility. Hides find their place in the furniture industry, where they are utilized in the creation of sofas, chairs, and upholstery to add a touch of luxury.
In the automotive sector, hides are employed in the manufacturing of car seats and steering wheel covers, enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and comfort of vehicles. Hides are utilized in the production of various home goods including pillows, cushions, and rugs, adding a touch of elegance to interior spaces. With such diverse applications and end products, hides continue to play a significant role in numerous industries.
| Difference Between Hide And Pelt |
|---|
| The term "hide" is used for the skins of larger animals like moose, cow, or deer. (Source: The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides) |
| Skin" is applied to smaller animals. (Source: The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides) |
| Fur" refers to a processed skin that retains its hair, often from bears, feline species, and mustelids. (Source: The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides) |
| Pelt" can be synonymous with fur or can be applied to an undressed skin that will become a fur. (Source: The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides) |
| Buckskin" is typically deer or sheep skin that has been tanned and stripped of all hairs. (Source: The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides) |
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between hide and pelt?
The difference between hide and pelt lies in their usage and the presence of fur. Hide refers to dried skin from animals, such as cow hide, and does not have the hair from the animal. On the other hand, a pelt is the skin from animals with fur or long hair still attached. It can be synonymous with fur or can be applied to an undressed skin that will become a fur.
How is the conditioning process different for hide and pelt?
The conditioning process for hide and pelt varies depending on their purpose. Hide, which is dried skin from animals, like cow hide, can be used to make leather. It undergoes a tanning process using various vegetable tannins or chemicals. In contrast, a pelt, which is the skin from animals with fur, often goes through a different process to retain its hair. This process involves fur-traders and specific techniques to preserve the fur while treating the skin.
What is the role of fur in an animal’s coat?
Fur plays a crucial role in an animal’s coat. It consists of three layers: down hair, awn hair, and guard hair. Down hair, the undercoat, provides insulation as it consists of wavy or curly hairs. Awn hair fills the gap between down and guard hairs, starting off growing like guard hairs but becoming wavy and thinner. Guard hairs, also known as the topcoat, are longer, straighter, and coarser than the other hairs. They provide protection and color to the coat.
How does the size of the animal affect the terms used for its fur coat?
The terms used to describe an animal’s fur coat can vary based on the animal’s size. The term “hide” is generally used for the skins of larger animals like moose, cow, or deer. On the other hand, “skin” is applied to smaller animals. This distinction helps differentiate between the size of the animal and its associated terminology.
Can you explain the difference between hair, fur, and wool?
Hair, fur, and wool are made from the same substance, keratin, and are chemically indistinguishable from each other. However, they are commonly used to describe specific types of covering. “Hair” is the term generally applied to humans, while “fur” is used for animals. Wool, on the other hand, refers specifically to a form of undercoat hair that is soft, curly, and never stops growing. It is primarily found in animals like sheep and goats.
Where can I learn more about tanning wild game pelts and hides?
If you want to learn more about tanning wild game pelts and hides, you can refer to “The Ultimate Guide to Tanning Wild Game Pelts and Hides.” This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on the tanning process and includes a glossary of related terms. It offers valuable insights into preserving and processing animal hides, skins, fur, and pelts.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – JamesDeMers from Pixabay
Image 1 By – Adbh266, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 2 By –