Mobility is the ability to move a joint actively, while flexibility is the range of motion a joint can passively achieve.
TL:DR Mobility Vs. Flexibility
Mobility focuses on both active movement and stability, allowing for efficient and functional movement patterns. It enhances performance in sports or daily activities by improving coordination, balance, and strength within that range of motion.
Flexibility primarily emphasizes passive stretching without necessarily incorporating stability or control. It aims to increase muscle length but may not address underlying imbalances or weaknesses that restrict optimal movement patterns.
What is Mobility?
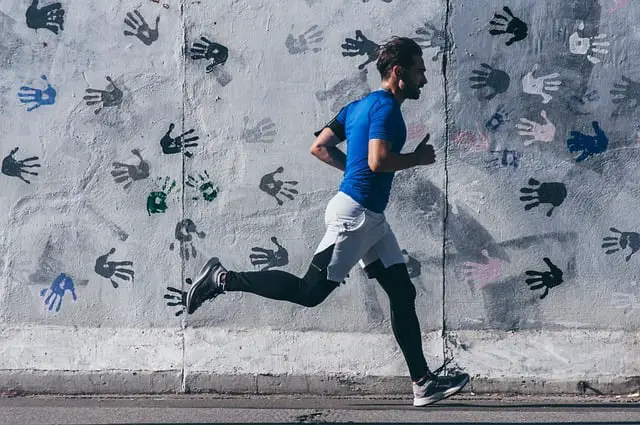

Mobility refers to the ability of our joints and muscles to move freely and efficiently through their full range of motion. It involves the coordination of various body parts working together seamlessly, allowing us to perform everyday activities with ease.
Mobility encompasses a broader spectrum. It includes factors such as joint stability, muscle strength, balance, and control. Think of it as the overall quality of movement.
Having good mobility means that you can squat down low without discomfort or reach overhead effortlessly. It allows you to twist your torso without straining your back and walk smoothly without any restrictions in your hips or knees.
Why is mobility important?
Well, improved mobility not only enhances athletic performance but also reduces the risk of injuries during physical activities. Lack of mobility can lead to imbalances in muscle strength and limited range of motion in certain areas, causing compensations elsewhere in the body.
How can we improve our mobility?
Regular exercises that target specific joints and muscle groups are key. Incorporating dynamic movements like lunges, squats, twists, and stretches into your fitness routine will help maintain or even enhance your current level of mobility.
What is Flexibility?
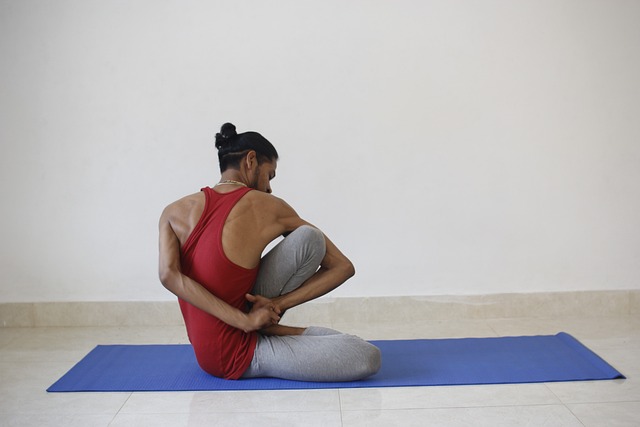

Flexibility is a vital component of physical fitness that refers to the range of motion in your joints and muscles. It allows you to move freely without any restrictions or discomfort. Having good flexibility can enhance performance in various activities, including sports, dance, and even everyday tasks.
One way to understand flexibility is by thinking about a rubber band. When a rubber band is stretched easily and returns to its original shape without any damage, it’s considered flexible. Similarly, when our muscles and joints can be stretched without causing pain or injury, we are said to have good flexibility.
Flexibility training involves stretching exercises that target specific muscle groups and improve their range of motion. These exercises may include static stretches where you hold a position for an extended period or dynamic stretches which involve continuous movement.
Having flexible muscles not only helps prevent injuries but also improves posture and balance. It allows us to perform movements with ease while reducing the risk of strain or sprain.
Flexibility refers to the ability of our muscles and joints to move through their full range of motion without any discomfort or limitations. Regular stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, leading to better physical performance and overall well-being
Mobility Vs. Flexibility – Key differences
| Aspect | Mobility | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to actively move a joint through its full range of motion. | The ability of a joint to passively move through its full range without resistance. |
| Involves | Active muscular control and joint stability during movement. | Passive elongation of muscles and stretching of connective tissues. |
| Type of Exercise | Enhances joint strength, stability, and control during movement. | Focuses on elongating muscles and increasing range of motion. |
| Range of Motion | Typically assessed in terms of functional movement and joint health. | Measured in terms of how far a joint can passively move without muscular effort. |
| Impacts Activities | Affects the quality of movements and sports performance. | Improves posture, reduces the risk of injury, and enhances overall flexibility. |
| Training Emphasis | Training includes exercises that challenge strength, balance, and coordination. | Training includes stretching, yoga, and static or dynamic stretching routines. |
| Muscular Activation | Requires muscular activation and control throughout the range of motion. | Involves minimal muscular activation, as muscles are stretched to their limits. |
Image Credits
Featured Image By – neo tam from Pixabay
Image 1 By – 117O8734 from Pixabay
Image 2 By – Amit N from Pixabay