Graphite is a soft mineral with a good electrical conductivity that can be used to make pencils due to its ability to leave marks on paper, while galena is a lead ore that has been used for centuries in jewellery and other applications.
Graphite
(Photo By James St. John on Flickr)
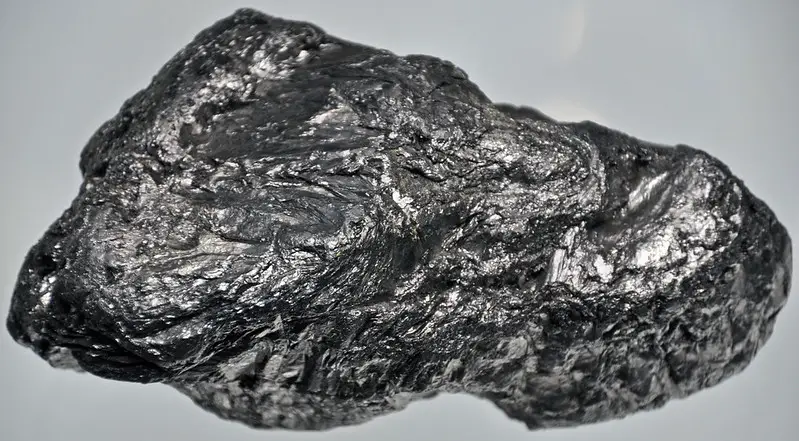

Graphite is a naturally occurring form of carbon that is widely used in industry and manufacturing. It is a mineral that forms when carbon is subjected to high pressure and high temperature over long periods of time. Graphite is known for its unique properties, including its ability to conduct electricity and heat, and its high strength-to-weight ratio.
Galena
(Photo By We Like Sharing on Flickr)
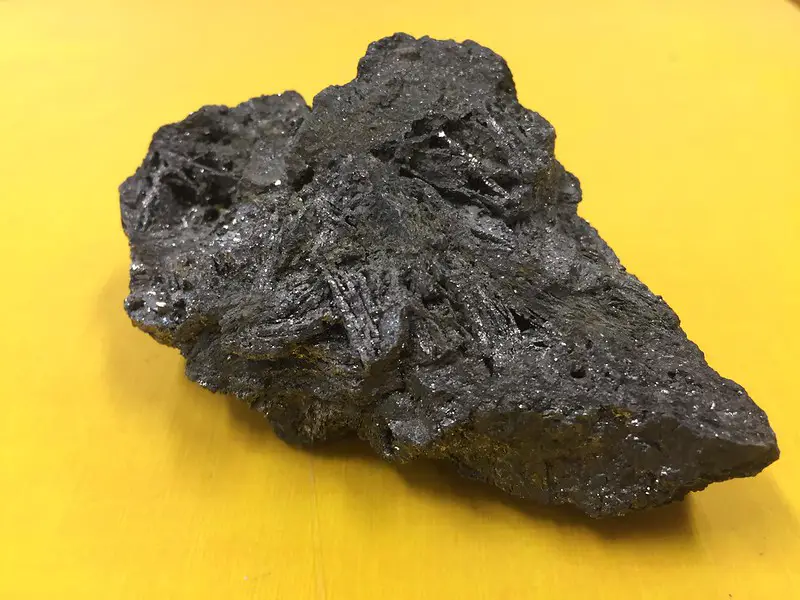

Galena is a naturally occurring lead sulfide mineral with a characteristic silver-gray color. It is the primary ore of lead and is often mined for its silver content. Galena has a relatively low melting point and is easily smelted to produce lead metal.
Galena is a lead sulfide mineral with a chemical composition of PbS. It is the primary ore mineral of lead. Galena is a common and popular mineral for rock hounds. Its characteristic cube-shaped crystals are easily recognized. They often have an interesting silvery-gray streak that adds to their beauty.
Galena has a relatively high density of 7.5-7.6 g/cm3, making it one of the heaviest minerals in nature. The hardness of galena is 2.5-3 on Mohs’ scale, making it rather soft and easy to scratch. Its cleavage is Poor/Indistinct, meaning that galena does not break along smooth planes like many other minerals do.
Galena typically occurs as cubic crystals, but can also be found in the form of octahedrons or dodecahedrons. It can sometimes be twinsned with another galena crystal to form various combinations, such as the star twin or mite twinning forms. Galena can also be found in massive form, as well as in compact and granular form when crystallization has been incomplete.
Galena is found in many parts of the world, but most notably in Europe and the Americas. The largest deposits are found in Peru, Bolivia, and Mexico. Deposits in the United States are found in Illinois, Missouri, Colorado, and Utah.
Properties of Graphite
Graphite is a naturally-occurring form of carbon. It is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions and is the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. Graphite has a wide range of properties that make it an important material in many industrial and technological applications.
Some of the most important properties of graphite include:
- High thermal conductivity: graphite is an excellent conductor of heat, making it useful in applications where thermal management is important.
- High electrical conductivity: graphite conducts electricity well, making it useful in electrical applications.
- Chemical stability: graphite is resistant to most acids and bases, making it chemically stable.
- Lubricity: graphite has a low coefficient of friction, making it an ideal lubricant.
- Resistance to wear: because of its lubricating properties, graphite experiences less wear than other materials.
Properties of Galena
Galena is a mineral composed primarily of lead sulfide (PbS). Some of its properties include:
- Color and luster: Galena is typically gray in color with a metallic luster, but can also be black or silver.
- Hardness: Galena is a relatively soft mineral, with a hardness of 2.5 on the Mohs scale.
- Density: Galena is a dense mineral, with a specific gravity of around 7.4 to 7.6.
- Cleavage: Galena has perfect cleavage in three directions, meaning it can be easily split into thin sheets.
- Crystal structure: Galena has a cubic crystal structure, with each cube face being a cleavage plane.
- Uses: Galena is primarily used as a source of lead, but it is also used in the manufacture of lead-acid batteries, ammunition, and some types of radiation shielding.
Toxicity: Galena is a toxic mineral, and prolonged exposure to lead and lead compounds can lead to serious health problems. It is important to handle galena and other lead-containing minerals with care and to take appropriate safety precautions.
Uses of Graphite
Graphite is a naturally-occurring form of crystalline carbon. It is a soft material that is used in a variety of applications, including pencils, lubricants, and brakes.
Pencils: Graphite is the material used in the lead of pencils. The lead is made up of fine graphite particles mixed with clay. The clay helps to hold the graphite together and gives the pencil its shape.
Lubricants: Graphite is often used as a lubricant because it is a dry lubricant. This means that it does not attract dust or dirt like some other lubricants do. Graphite is often used on door locks and in bicycles.
Brakes: Graphite is also used in brakes because it can create friction without wearing down the brake pads.
Uses of Galena
Galena is a lead sulfide mineral with a very low melting point. It is used in a variety of ways, including:
- As an ore of lead
- To make leaded glass
- In X-ray and gamma ray shielding
- As a source of sulfur for sulfuric acid production
- In the manufacture of paints, dyes, and inks
Difference Between Graphite and Galena
Graphite and galena are two minerals that are often confused for one another. They have similar physical properties, but there are some key differences that set them apart.
For one, graphite is a non-metal, while galena is a metal. This means that graphite is not conductive, while galena is. Additionally, graphite is much softer than galena—so soft, in fact, that it can be used as a lubricant. Galena, on the other hand, is quite brittle.
Another difference between the two minerals is their color. Graphite is typically black or dark gray, while galena can be silver-gray, blue-gray, or even greenish-gray. Finally, graphite has a naturally slippery surface, whereas galena does not.
How can you tell galena and graphite apart?
The two minerals are very different in appearance. Galena is a silver-gray mineral with a metallic luster, while graphite is a black mineral with a dull, sooty luster. If you were to touch each mineral, galena would feel heavy and have a greasy texture, while graphite would feel light and slippery.
To test for hardness, you can try scratching each mineral with your fingernail. Galena is much harder than graphite and will not scratch easily. Graphite, on the other hand, will easily leave a streak on your nail.
Another way to tell these minerals apart is by testing their conductivity. Galena is an excellent conductor of electricity, while graphite is not. To test this, simply touch each mineral with a piece of metal (like a penny). If the metal sticks to the galena, it’s because the electrical current has passed between them. This won’t happen with graphite.
What mineral is similar to graphite?
There are a few minerals that are similar to graphite in appearance, but the most similar would be galena. Galena is a lead sulfide mineral that has a silver-gray color and a high lustrous finish, just like graphite. It is also soft enough to be scratched with a fingernail and has a Mohs hardness of 2.5-3.0.
What are the types of graphite?
There are three primary types of graphite that occur naturally: flake, amorphous, and vein. Flake graphite is by far the most commercially important variety, comprising more than 80 percent of the natural graphite market. It is found as flat, platelet-like crystals that tend to flake off easily. These flakes can be extremely thin, often less than a micron in diameter. Amorphous graphite is the second most important natural variety and is found as fine particles embedded in sedimentary rocks such as coal. It has a lower carbon content than flake or vein graphite and is not as widely used commercially. The third type of natural graphite is vein graphite, which typically has the highest carbon content and is found in fractures and fissures in metamorphic rocks.
Featured Image By – (Photo By James St. John on Flickr)