Luster is shiny, reflecting light. Dull lacks shine, appearing matte. Both describe the appearance of surfaces, materials, or objects.
TL;DR Luster Vs. Dull
Luster refers to the way light reflects off a surface, creating a shiny or metallic appearance. On the other hand, dullness describes surfaces that lack shine or reflectivity.
Identifying luster involves observing how light interacts with an object’s surface and noting whether it appears shiny or reflective. Dullness is characterized by a lack of shine or reflection.
Luster
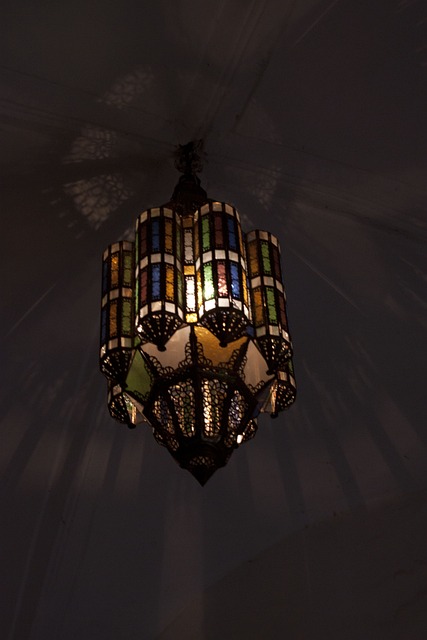

Luster refers to the quality of a surface that reflects light in a way that creates a shiny, glossy, or reflective appearance. It is often used to describe the visual quality of minerals, metals, and other materials.
Dull
Dullness is the absence of shine or glossiness in a surface or object. It lacks the ability to reflect light in a way that creates a bright or shiny appearance, often resulting in a flat or matte visual quality.
Luster Vs. Dull – Key differences
| Property | Luster | Dull |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Shiny, glossy, reflective | Lack of shine, matte |
| Light | Reflects light, creating brightness | Absorbs or scatters light |
| Surface | Smooth and reflective | Often rough or non-reflective |
| Examples | Polished metal, glass | Unpolished wood, paper |
| Visual | Attractive, attention-catching | Subdued, less attention-grabbing |
What is luster in chemistry?
Luster in chemistry refers to the way a mineral or substance reflects light. It describes how shiny or reflective the surface of an object appears when it interacts with light.
The intensity and quality of luster can vary greatly, ranging from highly reflective and metallic to dull and non-reflective.
Different types of luster include metallic, adamantine (diamond-like), vitreous (glassy), pearly, silky, greasy, waxy, resinous, and earthy.
Metallic luster is characterized by its high reflectivity and resemblance to metals like gold or silver. Adamantine luster is extremely bright and sparkling like that seen in diamonds.
How do you identify luster?
- Observation: Examine the surface of the material or object under a good light source.
- Reflection: If the surface reflects light brightly and appears shiny and glossy, it likely has luster.
- Clarity: Lustrous surfaces will show clear and distinct reflections, often resembling a mirror-like quality.
- Intensity: The intensity of the reflected light can vary. Some materials may have a high luster, reflecting light strongly, while others might have a more subdued or moderate luster.
- Smoothness: Luster is often associated with smooth surfaces that allow light to bounce off without scattering. Rough surfaces tend to have less pronounced luster.
- Variability: Different materials can exhibit different types of luster, such as metallic, vitreous (glass-like), pearly, or silky.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Med Ahabchane from Pixabay
Image 1 By – Amel Qahwadji from Pixabay