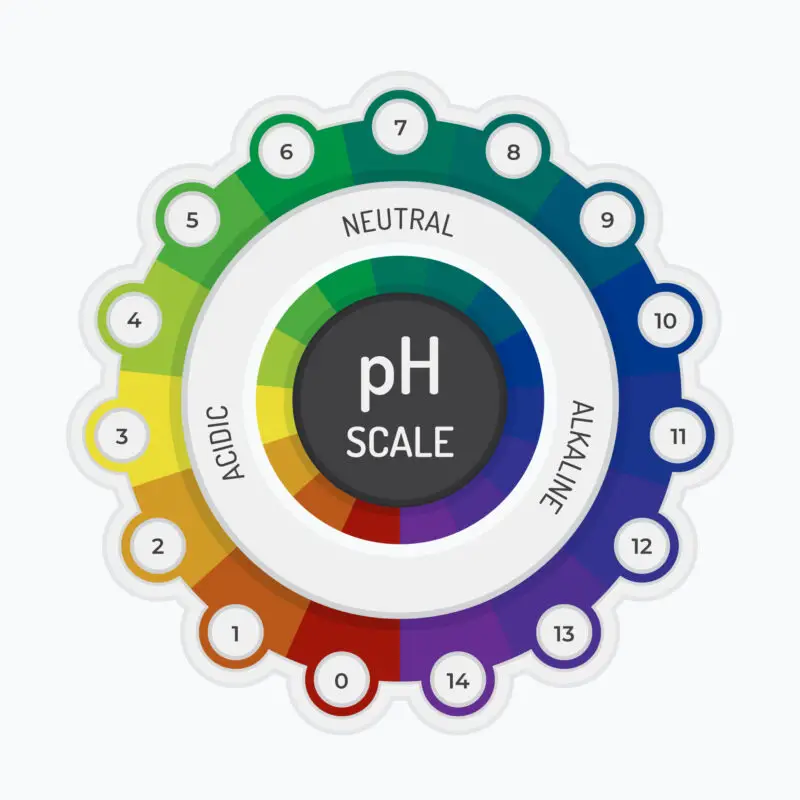
Acidity of water refers to a pH below 7 due to an excess of hydrogen ions, while alkalinity indicates a pH above 7 due to an excess of hydroxide ions or other bases.
Acidity Vs. Alkalinity
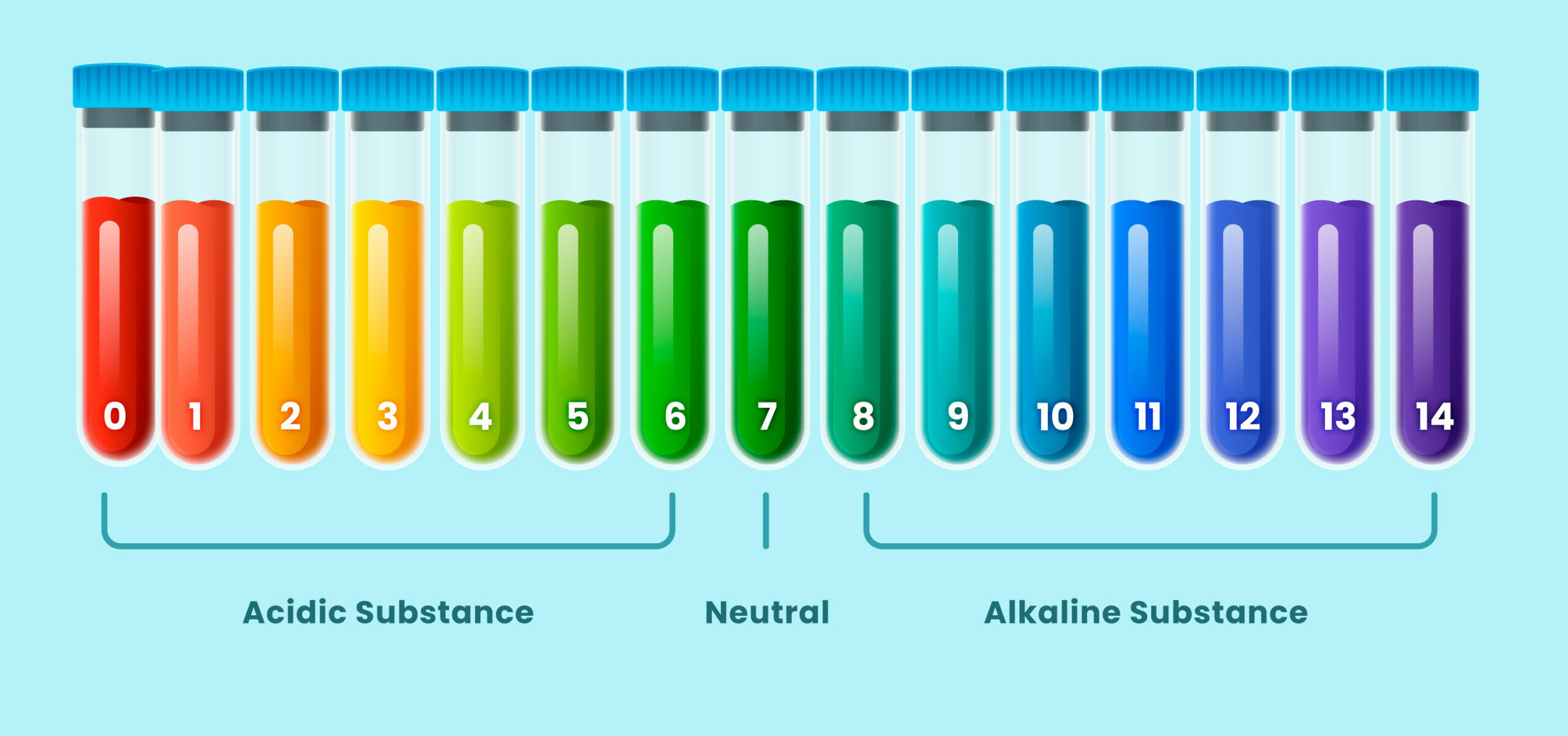
- pH below 7 | pH above 7.
- Excess of hydrogen ions (H+) | Excess of hydroxide ions (OH-) or other bases.
- Water with acidic properties | Water with basic or alkaline properties.
- Can be neutralized by adding bases | Can be neutralized by adding acids.
Acidic water
Acidic water is characterized by a pH level below 7, indicating an increased concentration of hydrogen ions. This low pH can result from various factors such as dissolved carbon dioxide or the presence of certain minerals in the water source.
One common cause of acidity in water is acid rain. When pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides mix with moisture in the atmosphere, they form acidic compounds that eventually fall back to earth as rainwater. This can lead to lower pH levels in natural bodies of water and even affect groundwater sources.
Acidic water may have some noticeable effects. It might taste slightly sour or metallic and could potentially corrode metal pipes over time due to its corrosive properties. Additionally, it may impact aquatic life if discharged directly into streams or lakes without proper treatment.
Alkaline water
Alkaline water refers to water that has a higher pH level than regular tap water. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Alkaline water typically has a pH level of around 8 or 9, making it slightly basic.
One possible benefit of drinking alkaline water is its ability to help balance the body’s acidity levels. It is believed that consuming too many acidic foods and beverages can contribute to an imbalance in the body’s pH levels, leading to various health issues. Drinking alkaline water may help neutralize excess acid in the body and restore balance.
Another potential advantage of alkaline water is its antioxidant properties. Some studies suggest that alkaline water may have antioxidant effects, which can help protect against oxidative stress and free radicals in the body.
Acidity Vs. Alkalinity of water – Key differences
| Acidity | Alkalinity |
|---|---|
| pH below 7 | pH above 7 |
| Excess of hydrogen ions (H+) | Excess of hydroxide ions (OH-) or other bases |
| Higher concentration of H+ ions | Higher concentration of OH- ions or other bases |
| Water has acidic properties | Water has basic or alkaline properties |
| Acidic water can be neutralized by adding bases | Alkaline water can be neutralized by adding acids |
| Lemon juice, vinegar | Baking soda solution, soapy water |
| Acidic water can be corrosive to metals | Alkaline water can also be corrosive in high concentrations |
| Acidic water can harm aquatic life and ecosystems | Alkaline water can affect water hardness and pH stability |
How to test the acidity or alkalinity of water
Testing the acidity or alkalinity of water is crucial to ensure its quality and suitability for various purposes.
- Litmus paper: One of the easiest ways to test water pH is by using litmus paper strips. Dip a strip into the water sample and compare its color change with a provided chart indicating acidic, neutral, or alkaline levels.
- pH testing kit: Purchase a pH testing kit from a local store or online retailer. These kits typically include reagents and instructions for accurate measurements. Follow the guidelines carefully to obtain reliable results.
- Electronic pH meter: For more precise readings, invest in an electronic pH meter specifically designed for water analysis. This device measures the voltage generated when immersed in a liquid and displays corresponding pH values on its screen.
- Natural indicators: Certain natural substances can act as indicators of acidity or alkalinity in water. For example, red cabbage juice turns pink/red in acidic solutions and green/blue in alkaline solutions.
Remember that different applications may require specific ranges of acidity or alkalinity, so it’s essential to know what level is suitable for your intended use (e.g., drinking, gardening). Regularly monitoring your water’s pH will help maintain optimal conditions for various activities while safeguarding health and environment alike.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Image by Freepik
Image 1 By – Image by Freepik