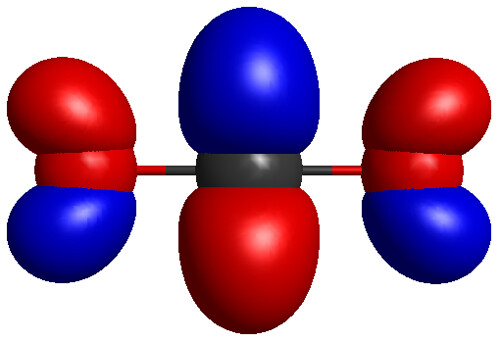
Bond polarity refers to the unequal sharing of electrons in a chemical bond, while molecular polarity is the overall distribution of charge in a molecule.
TL;DR Bond polarity Vs. Molecular polarity
Bond polarity is the uneven sharing of electrons between atoms in a chemical bond, determined by electronegativity. Molecular polarity is the overall distribution of charge in a molecule, resulting from an asymmetrical arrangement of bonds or electron pairs.
What is Bond Polarity?
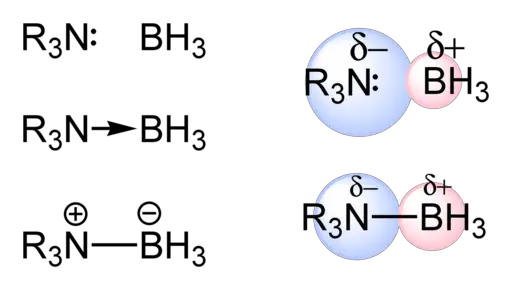
Bond polarity refers to the uneven sharing of electrons between atoms in a chemical bond. It is determined by the difference in electronegativity values of the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself.
In a covalent bond, where two non-metal atoms share electrons, if the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is small or nonexistent, the bond is considered nonpolar. This means that both atoms have an equal pull on the shared electrons.
What is Molecular Polarity?
Molecular polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons within a molecule, resulting in regions of partial positive and negative charges. This occurs when there is an asymmetrical arrangement of atoms or electron pairs around the central atom.
In simpler terms, molecular polarity determines whether a molecule has a positive and negative end (like a magnet) or if it’s evenly balanced throughout. It influences various properties such as solubility, boiling points, and interactions with other molecules.
Bond polarity Vs. Molecular polarity – Key differences
Bond Polarity
- Definition: Bond polarity refers to the uneven sharing of electrons between two atoms in a chemical bond. It occurs when the electronegativity of the atoms involved is different.
- Focus: It focuses on individual chemical bonds within a molecule and describes the distribution of charge within that specific bond.
- Result: Bond polarity results in a partial positive charge (+δ) on the less electronegative atom and a partial negative charge (-δ) on the more electronegative atom, creating a dipole moment.
- Classification: Bond polarity can be categorized as nonpolar covalent (equal sharing of electrons), polar covalent (unequal sharing of electrons), or ionic (complete transfer of electrons).
Molecular Polarity
- Definition: Molecular polarity refers to the overall distribution of charge in a molecule, considering the arrangement of all bonds and lone pairs in the molecule.
- Focus: It considers the entire molecule as a whole and describes the resulting polarity based on the sum of individual bond polarities.
- Result: Molecular polarity occurs when there is an asymmetrical arrangement of polar bonds or lone pairs, leading to a net dipole moment.
- Classification: Molecules can be classified as polar (net dipole moment) or nonpolar (no net dipole moment) based on their overall geometry and the nature of their individual bonds.
Bond polarity describes the uneven sharing of electrons in a specific chemical bond, Molecular polarity considers the overall charge distribution in the entire molecule.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – ChiralJon on Flickr
Image 1 By – Benjah-bmm27, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons