Sea breeze is daytime, from sea to land, cool; land breeze is nighttime, from land to sea, warm. Result from temperature differences.
TL;DR Land breeze Vs. Sea breeze
A sea breeze is a refreshing wind that blows from the cooler ocean or lake towards the warmer land during the day. It brings relief from heat and humidity, making it a favorite among beachgoers seeking relief on hot summer days. The sea breeze results from the air over the water being relatively cooler than over adjacent land areas due to differential heating.
A land breeze occurs at night when cooler air moves from higher pressure inland regions towards lower pressure coastal areas. This phenomenon reverses the direction of airflow compared to a sea breeze, with winds blowing offshore instead of onshore. Land breezes are typically weaker than their daytime counterparts but can still have an impact on local weather conditions.
What is a Sea Breeze?
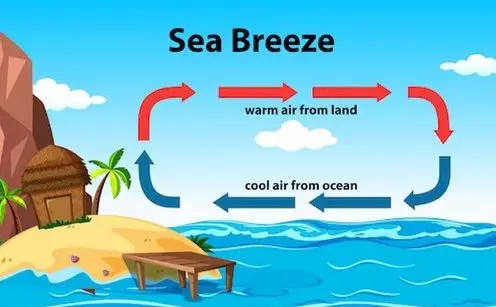
Sea breeze, as the name suggests, is a refreshing wind that originates from the sea and flows towards the land. It occurs during the daytime when there is a temperature difference between the ocean surface and adjacent coastal areas. This phenomenon is primarily influenced by solar radiation.
Here’s how it works: during daylight hours, the sun heats up both land and water surfaces. However, due to its higher heat capacity, water takes longer to warm up compared to land. As a result, the air above the land becomes warmer than the air above the sea.
As warm air rises over heated land masses, cooler air from overlying water rushes in to fill this void. This movement of relatively cooler maritime air inland creates what we call a sea breeze.
The strength of a sea breeze depends on various factors such as temperature gradients between land and sea, atmospheric pressure patterns, coastal topography, and proximity to large bodies of water. In general terms though, it tends to be gentler than other types of winds.
Sea breezes are not only pleasant but also have important implications for local climates and ecosystems along coastlines worldwide. They provide relief from sweltering temperatures in beach towns during hot summer days while aiding in pollination processes for plants growing near shorelines.
What is a Land Breeze?
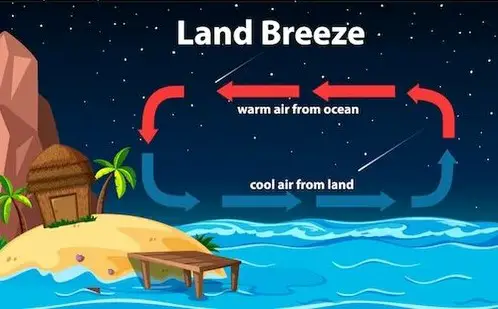
As the name suggests, it is a type of wind that blows from the land towards the sea during the night.
During daytime, as you may already know, the sun heats up both land and water surfaces. However, land tends to heat up faster than water due to its lower heat capacity. As a result, air over the land becomes warmer and rises while cooler air from above moves in to replace it – commonly known as a sea breeze.
At nightfall, things start to change. The land cools down more rapidly than water because it loses heat faster due to its lower specific heat capacity. This leads to a reversal of roles: now that cooler air resides overland and warmer air hovers above water.
The temperature difference between these two surfaces creates an area of high pressure overland and low pressure overwater – which prompts winds from high-pressure regions (the land) towards low-pressure regions (the sea). These winds are referred to as “land breezes.”
Land breezes typically occur after sunset when there is minimal heating from sunlight on both sides. Unlike sea breezes that generally blow during daylight hours when temperatures peak.
Land breeze Vs. Sea breeze – Key differences
| Aspect | Land Breeze | Sea Breeze |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | Nighttime, after sunset | Daytime, during and after sunrise |
| Direction | Blows from land toward the sea | Blows from the sea toward the land |
| Temperature | Warmer than the sea, as land cools quickly | Cooler than the land, as the sea retains heat |
| Cause | Land cools more rapidly than the sea after sunset, creating a pressure difference | Land heats up faster than the sea during the day, leading to a pressure difference |
| Strength | Generally weaker and less consistent | Often stronger and more predictable |
| Effects | Typically brings warmer, drier air to the coast | Brings cooler, moister air from the sea to the land, potentially leading to cloud formation |
| Impact on Weather | Can contribute to clear nights and temperature drops | Can moderate temperatures and influence cloud cover, common near coastal regions |
| Geography | Common in coastal areas with a noticeable temperature difference between land and sea | Prevalent along coasts and large bodies of water with significant temperature variations |
| Nautical Use | Historically used by sailors for night navigation | Often used for daytime sailing, providing predictable wind patterns |
Image Credits
Featured Image By – PowerLee from Pixabay
Image 1 By – brgfx, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Image 2 By – brgfx, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons









