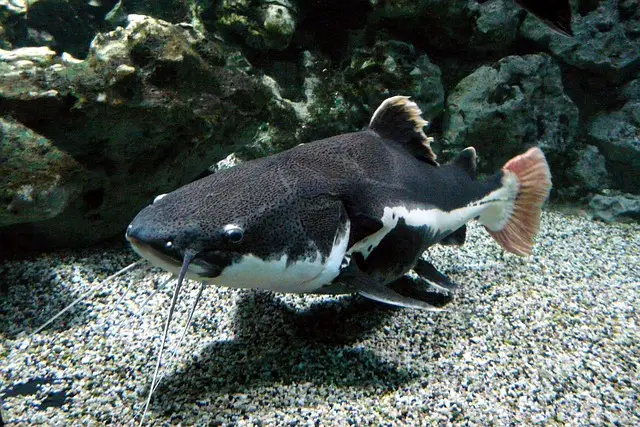
Catfish typically have prominent barbels and flat heads, while mudfish have elongated bodies with dorsal and anal fins set back towards the tail.
Did you know that catfish and mudfish, two common freshwater fish, have distinct differences that set them apart? From their physical characteristics to their habitat preferences, understanding the disparities between these two species can help you appreciate the diverse world of aquatic life. In this article, we’ll dive into the key distinctions between catfish and mudfish, providing insights into their appearance, size, behavior, and more. Whether you’re an avid angler or simply curious about the wonders of nature, this comparison will shed light on the unique qualities of catfish and mudfish.
Key Takeaways:
- Catfish and mudfish are both freshwater fish with remarkable differences in physical appearance, size, habitat preferences, dietary habits, and reproductive strategies.
- Physical characteristics such as barbels, skin texture, head shape, and body structure help distinguish catfish from mudfish.
- Catfish can grow to impressive sizes, with some species reaching lengths of up to 10 feet, while mudfish typically average around 12 to 16 inches in length.
- Catfish are adaptable to both freshwater and saltwater environments, while mudfish thrive primarily in freshwater habitats such as marshes and muddy areas.
- Catfish are bottom-dwellers with a varied diet that includes insects, crustaceans, and small fish, whereas mudfish are carnivorous predators that feed on other fish, crayfish, and insects.
Physical Characteristics
When distinguishing between catfish and mudfish, their physical characteristics play a significant role. Catfish have distinct features that set them apart from mudfish. Here are the key differences:
Catfish Characteristics:
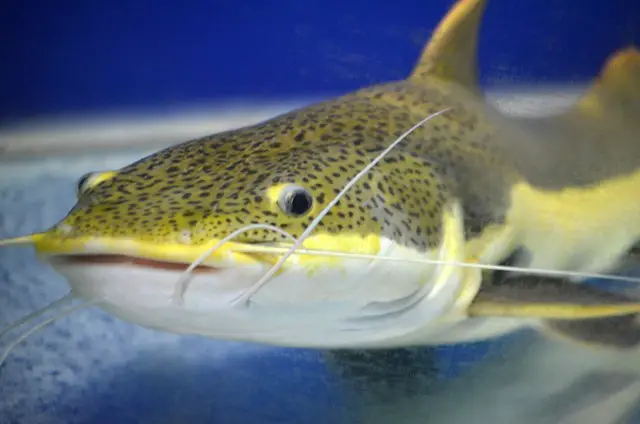

- Long, whisker-like barbels around their mouths
- Smooth and scaleless skin
- Broad and flattened head
- Muscular body
Mudfish Characteristics:
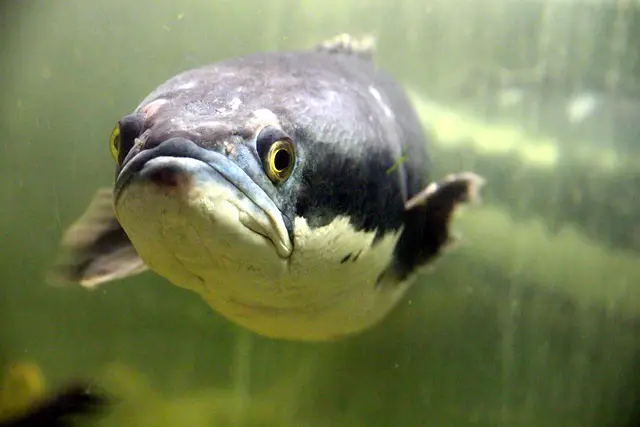

- Elongated bodies
- Long dorsal fins
- Scale-covered skin
- Sharp teeth
These physical attributes make it easy to distinguish between catfish and mudfish at a glance.
| Catfish | Mudfish |
|---|---|
| Whisker-like barbels | Long dorsal fins |
| Smooth and scaleless skin | Scale-covered skin |
| Broad and flattened head | Sharp teeth |
| Muscular body | Elongated bodies |
The table above provides a visual representation of the distinguishing physical characteristics between catfish and mudfish.
Size Differences
When comparing catfish and mudfish, one noticeable difference is their size. Let’s take a closer look at the variations between these two species:
| Catfish | Mudfish |
|---|---|
| Catfish can vary in size depending on the species, with some reaching lengths of up to 10 feet and weights of over 600 pounds. | Mudfish, on the other hand, are usually smaller, averaging around 12 to 16 inches in length. |
| However, some mudfish species can grow up to 3 feet in length. |
As you can see, catfish are generally larger than mudfish, with some species reaching impressive sizes. While mudfish may not match the size of their catfish counterparts, they can still grow to respectable lengths, especially certain species. It’s important to consider these size differences when distinguishing between catfish and mudfish in the wild.
Habitat Preferences
When it comes to their habitat preferences, catfish and mudfish exhibit significant contrasts. Let’s explore the distinct environments these two species can be found in.
Catfish
Catfish are incredibly versatile and can inhabit both freshwater and saltwater environments. They are commonly found in rivers, lakes, and ponds, making them a popular catch for anglers. These fish have a preference for areas with abundant vegetation and underwater structures, as they provide ample hiding spots and food sources.
In saltwater environments, catfish can be found in coastal areas and estuaries, often near the mouth of rivers where freshwater meets the sea. They possess unique adaptations that allow them to survive in both freshwater and saltwater, making them highly adaptable to various aquatic ecosystems.
Mudfish
Mudfish, also known as bowfin, have more specific habitat preferences. They are primarily found in freshwater environments such as muddy or swampy areas, marshes, and flooded fields. These fish have a remarkable ability to tolerate low oxygen levels and can survive in stagnant or poorly oxygenated waters.
Their preference for muddy and swampy areas is evident in their ability to navigate through thick vegetation and shallow waters. Mudfish often thrive in habitats rich in aquatic plants and submerged timber, as these provide cover and breeding grounds. By contrasting the habitat preferences of catfish and mudfish, it becomes clear that they have distinct niches within freshwater ecosystems. While catfish thrive in a variety of environments, mudfish have adapted to specific habitats that suit their unique characteristics.
Dietary Habits
While catfish and mudfish both inhabit freshwater environments, they have distinct dietary preferences that contribute to their unique ecological roles.
Similarities
- Both catfish and mudfish play important roles in their respective ecosystems by helping to regulate populations of smaller organisms.
Differences
Catfish are opportunistic bottom-dwellers, using their sensitive barbels to locate food sources:
- Insects
- Crustaceans
- Small fish
- Plant matter
Mudfish, on the other hand, have a more carnivorous diet and feed on:
- Other fish
- Crayfish
- Insects
These differences in dietary habits allow both species to occupy distinct niches within their ecosystems, contributing to overall biodiversity and ecological balance.
Reproductive Strategies
When it comes to reproduction, catfish and mudfish have distinct strategies that set them apart. Let’s take a closer look at how these freshwater fish reproduce:
Reproduction Method of Catfish
Catfish employ external fertilization and reproduce by laying adhesive eggs on surfaces like rocks or vegetation. After the eggs are laid, male catfish often take on the role of guardians, protecting the eggs until they hatch. This parental care ensures the survival and well-being of the developing offspring.
Remarkably, some catfish species exhibit mouthbrooding behavior. In these cases, the female catfish holds the fertilized eggs in her mouth until they hatch. This unique reproductive strategy allows for increased protection against predators and ensures the optimal development of the young catfish.
Reproduction Method of Mudfish
Unlike catfish, mudfish employ internal fertilization for reproduction. During mating, males transfer sperm to the female’s reproductive system. The female then releases the fertilized eggs into the water. This method of reproduction provides mudfish with greater control over the fertilization process and enables them to adapt to various environmental conditions.
Overall, the reproductive strategies of catfish and mudfish showcase their remarkable adaptations to their respective habitats. While catfish rely on external fertilization and parental care, mudfish employ internal fertilization, highlighting the diversity and ingenuity found within the fish kingdom.
| Catfish Reproduction | Mudfish Reproduction |
|---|---|
| External fertilization | Internal fertilization |
| Adhesive eggs | Release fertilized eggs into the water |
| Male guardianship | N/A |
| Mouthbrooding behavior (in some species) | N/A |
Nutritional Composition
Catfish and mudfish are both nutritious options that offer unique culinary experiences. While they share similar protein content, their fat composition sets them apart. Catfish are known for their rich, oily texture, while mudfish have a leaner profile. Both species provide valuable nutrients and can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
Protein Content
Both catfish and mudfish are excellent sources of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining overall health. Protein also helps to keep you feeling full and satisfied, making it an important component of a balanced meal.
Fat Composition
The main difference between catfish and mudfish lies in their fat content. Catfish are known for their higher fat content, which contributes to their oily texture. This can add a rich and flavorful element to culinary preparations. Mudfish, on the other hand, have a leaner fat profile, making them a lighter option for those seeking a lower-fat seafood choice.
Vitamins and Minerals
In addition to protein and fat, catfish and mudfish are good sources of various vitamins and minerals. These include vitamin B12, which is important for brain health and the production of red blood cells, as well as selenium, a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function. Other minerals found in both fish species include phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium.
When incorporating catfish or mudfish into your diet, it’s important to consider the cooking methods and seasonings used, as these can affect the overall nutritional profile of the dish. Grilling, baking, or steaming the fish can help to maintain the nutritional integrity while minimizing added fats or calories. Pairing the fish with nutrient-rich vegetables and whole grains can further enhance the overall nutritional value of your meal.

Blue Catfish
Blue catfish are large freshwater fish found in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. Some can weigh over 100 pounds, making them a popular catch for fishermen. They have forked tails and are colored slate blue on top and white on their bellies.
To catch blue catfish, it’s important to know where they live and how they behave. They prefer deep areas with plenty of hiding spots and food sources. They eat a variety of things, like other fish and insects, so using the right bait and fishing in the right places increases your chances of catching one.
To help you gain a better understanding of the behavior and characteristics of blue catfish, take a look at the table below:
| Blue Catfish Facts | Blue Catfish Behavior |
|---|---|
| Found in large rivers, lakes, and reservoirs | Favor deep pools and channels |
| Can grow to over 100 pounds | Opportunistic feeders |
| Forked tail | Active predators |
| Coloration ranges from slate blue to white | Migrate to spawn |
Blue Catfish Facts:
- Blue catfish are primarily found in large rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
- They can grow to impressive sizes, with some individuals exceeding 100 pounds.
- Blue catfish have forked tails and their coloration ranges from slate blue on the back to white on the belly.
Blue Catfish Behavior:
- Blue catfish favor deep pools and channels in their habitats.
- They are opportunistic feeders, consuming a wide variety of prey.
- Blue catfish are active predators, constantly searching for food.
- They migrate to spawn, often traveling long distances.
Channel Catfish
Channel catfish are abundant in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, ranking second only to bass in popularity among anglers. They have an olive-brown to slate coloration with small black spots. Channel catfish have a deeply forked tail and are known for their excellent table fare. Using the right baits and techniques can enhance the chances of catching these sought-after fish.
When targeting channel catfish, it’s important to understand their habits and preferences. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Habitat:
Channel catfish can be found in a variety of freshwater habitats, including deep pools, slow-moving rivers, and reservoirs. They are often found near submerged logs, rocky areas, and undercut banks, where they seek shelter and ambush their prey.
Feeding Habits:
Channel catfish are opportunistic feeders and will consume a wide range of prey items. They primarily feed on small fish, insects, crustaceans, and even plant matter. Knowing what channel catfish are feeding on in your specific location can help you choose the most effective bait.
Best Baits:
When targeting channel catfish, it’s crucial to use baits that will entice them to bite. Some popular options include live baits like nightcrawlers, minnows, and cut bait (such as pieces of fish). Prepared baits, such as stink baits or dough baits, can also be effective. Experimenting with different baits and techniques is key to finding what works best in your particular fishing spot.
Fishing Techniques:
There are several techniques that can be effective for catching channel catfish. Bottom fishing with a sinker and baited hook is a popular method. You can also try drift fishing, where you let your bait drift naturally with the current. Another technique is using a slip bobber rig, which allows you to suspend your bait at a desired depth. Additionally, using scent-based attractants or adding attractant sprays to your baits can help increase your chances of success.
By understanding the habitat, feeding habits, and preferred baits and techniques, you can increase your chances of landing channel catfish. Whether you’re an experienced angler or just starting out, targeting these fish can provide an exciting and rewarding fishing experience.
| Channel Catfish Information | Channel Catfish Habits |
|---|---|
| Abundant in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs | Opportunistic feeders |
| Olive-brown to slate coloration with small black spots | Prefer deep pools, slow-moving rivers, and areas with submerged logs |
| Deeply forked tail | Feeds on small fish, insects, crustaceans, and plant matter |
| Known for their excellent table fare | Effective baits include live baits like nightcrawlers and minnows, as well as prepared baits |
| Bottom fishing, drift fishing, slip bobber rigs, and attractant sprays are effective techniques |
Conclusion
Catfish and mudfish are two types of freshwater fish that have different traits in how they look, how big they get, where they live, what they eat, how they have babies, and what they’re made of. Knowing these differences is important for telling them apart and understanding their place in nature.
For people who like fishing, knowing the details about catfish and mudfish can make their fishing trips more exciting. Each fish might need a different kind of bait or fishing method to catch them. Knowing where they like to hang out can help fishermen find them easier. And for people who enjoy cooking, learning about catfish and mudfish opens up a whole world of delicious recipes. Each fish has its own taste and texture, giving cooks plenty of options to explore. Whether you prefer the rich flavor of catfish or the tender meat of mudfish, these freshwater treasures are sure to satisfy your appetite.
FAQ
What are the key differences between catfish and mudfish?
Catfish and mudfish have different habitat preferences, physical characteristics, dietary habits, and reproductive strategies.
How can you distinguish catfish and mudfish based on their physical characteristics?
Catfish have long whisker-like barbels, smooth and scaleless skin, a broad and flattened head, and a muscular body. Mudfish, on the other hand, have elongated bodies, long dorsal fins, scale-covered skin, and sharp teeth.
Are there differences in size between catfish and mudfish?
Yes, catfish can vary in size depending on the species, with some reaching lengths of up to 10 feet and weights of over 600 pounds. Mudfish are usually smaller, averaging around 12 to 16 inches, but some species can grow up to 3 feet.
What are the habitat preferences of catfish and mudfish?
Catfish are found in both freshwater and saltwater environments such as rivers, lakes, and ponds. They prefer areas with abundant vegetation and underwater structures. Mudfish, on the other hand, are primarily found in freshwater habitats like muddy or swampy areas, marshes, and flooded fields.
What type of diet do catfish and mudfish have?
Catfish are bottom-dwellers and feed on insects, crustaceans, small fish, and plant matter. Mudfish are carnivorous and feed on prey like other fish, crayfish, and insects.
How do catfish and mudfish reproduce?
Catfish lay adhesive eggs on surfaces like rocks or vegetation, with some species exhibiting mouthbrooding behavior. Mudfish employ internal fertilization, with males transferring sperm to the female’s reproductive system.
Are there any differences in the nutritional composition of catfish and mudfish?
Both catfish and mudfish are valuable sources of nutrients, but they differ in fat composition. Catfish are known for their oily texture.
Can you provide information about blue catfish?
Blue catfish are primarily found in large rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. They can reach impressive sizes, with some individuals exceeding 100 pounds. Blue catfish have forked tails and range in color from slate blue on the back to white on the belly.
What are some facts about channel catfish?
Channel catfish are abundant in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs. They have an olive-brown to slate coloration with small black spots. Channel catfish have a deeply forked tail and are known for their excellent taste.
In conclusion, what are the key takeaways about catfish and mudfish?
Catfish and mudfish are distinct species of freshwater fish with unique characteristics in terms of physical appearance, size, habitat preferences, dietary habits, reproductive strategies, and nutritional composition. Understanding these differences enhances our knowledge and appreciation of aquatic life.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – U Hd from Pixabay
Image 1 By – PublicDomainPictures from Pixabay