Thymus is a lymphoid organ for immune function, while thyroid is an endocrine gland regulating metabolism. Both have distinct roles in the body.
TL:DR Thymus Glands Vs. Thyroid Gland
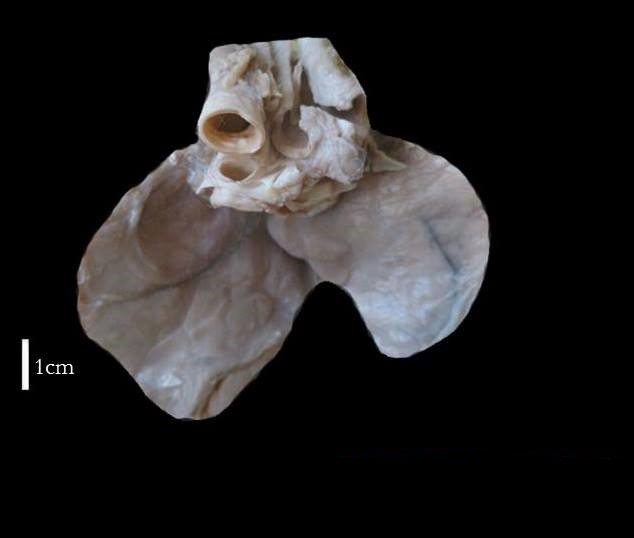
The thymus gland is located in the upper chest region behind the sternum. It plays a crucial role in supporting our immune system by producing T-cells which help fight off infections and diseases. The thymus gland is most active during childhood but gradually decreases in size as we age.
On the other hand, the thyroid gland is situated at the base of our neck just below the Adam’s apple. It regulates metabolism by producing hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones control various bodily functions including heart rate, digestion, energy levels, and growth.
What is the Thymus Gland?
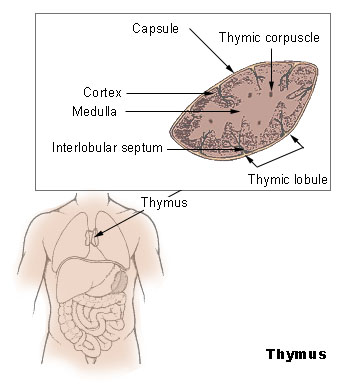
The thymus is a crucial lymphoid organ located in the upper chest. Primarily active during childhood and adolescence, it plays a central role in the immune system’s development.
The thymus produces and matures T lymphocytes (T cells), essential for immune responses against infections and abnormal cells. Over time, the thymus involutes or shrinks, becoming less active in adulthood.
Despite its reduced size, it remains essential for maintaining immune function and is integral in ensuring the body’s ability to mount effective defenses against pathogens throughout life.
What is The Thyroid Gland?
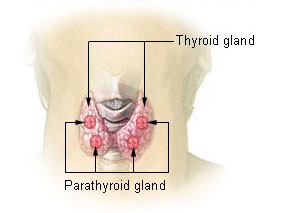
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland situated in the neck. It produces hormones, predominantly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which regulate metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
These hormones influence various physiological processes, including heart rate, growth, and metabolism of nutrients.
Controlled by the pituitary gland, the thyroid maintains a delicate hormonal balance crucial for overall health. Imbalances, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can lead to diverse health issues. The thyroid’s intricate hormonal control system underscores its vital role in maintaining homeostasis and influencing the proper functioning of multiple organ systems.
Thymus Glands Vs. Thyroid Gland – Key differences
| Feature | Thymus Gland | Thyroid Gland |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Upper chest | Neck |
| Shape | Lobular, bilobed | Butterfly-shaped |
| Function | Immune system development, T cell maturation | Regulates metabolism, produces thyroid hormones |
| Hormones Produced | None (primarily involved in immune function) | Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) |
| Activity Period | Mainly active during childhood and adolescence | Active throughout life, controlled by pituitary gland |
| Role in Immune System | Central in T cell development and maturation | Not directly involved in immune system development |
| Size Changes Over Time | Involutes or shrinks with age | Can vary in size but does not involute significantly |
| Regulation | Not regulated by pituitary gland | Regulated by pituitary gland through thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) |
| Associated Disorders | Thymic hyperplasia, myasthenia gravis | Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, thyroid nodules |
| Overall Impact on Health | Critical for immune system function | Crucial for metabolic regulation and overall physiological balance |
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Dr. Roshan Nasimudeen, CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Image 1 By – public domain
Image 2 By – public domain