Sunburn is a common form of skin damage caused by prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays, resulting in redness, pain, and peeling. Sun poisoning refers to a more severe reaction to excessive sun exposure that can lead to systemic symptoms like fever, nausea, and headache.
What is Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning, also known as sun rash or polymorphic light eruption (PMLE), is a severe form of sunburn that affects some individuals more than others. Unlike regular sunburn, which primarily affects the outer layer of the skin, sun poisoning extends deeper into the layers beneath. This can result in more intense symptoms and longer recovery times.
The main cause of sun poisoning is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. People with fair skin are particularly susceptible to this condition due to their lower levels of melanin, which provides natural protection against UV rays. However, anyone can develop sun poisoning if they spend excessive time under direct sunlight without proper protection.
Symptoms of sun poisoning can vary but often include severe redness and blistering on exposed areas such as the face, neck, arms, and legs. In addition to these visible signs, individuals may experience intense pain and discomfort accompanied by fever, chills, headache, nausea or vomiting.
If left untreated or ignored for too long a period before seeking medical attention you may risk developing complications like dehydration or infection from open blisters caused by severe cases of Sun Poisoning.
To prevent sun poisoning it’s important to take proactive measures such as applying sunscreen with a high SPF regularly throughout the day & limit your time outside between 10 am-4 pm when UV rays are strongest.
Aside from using sunscreen , wearing protective clothing like wide-brimmed hats , sunglasses & seeking shade whenever possible will help minimize your risk . Remember that prevention is key when it comes to protecting yourself from harsh UV rays .
What is Sunburn?
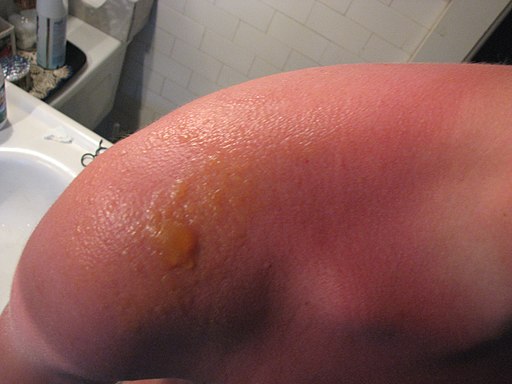
Sunburn is a common skin condition that occurs when the skin gets overexposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. It typically causes redness, pain, and peeling of the affected areas. Sunburn can happen to anyone, regardless of their skin color or type.
The main cause of sunburn is prolonged exposure to UV rays without proper protection, such as sunscreen or protective clothing. When you spend too much time in the sun without adequate protection, the UV rays penetrate your skin and damage its cells. This triggers an inflammatory response in your body, leading to the characteristic symptoms of sunburn.
Symptoms of sunburn usually appear within a few hours after excessive sun exposure and worsen over 24-48 hours. The affected area may feel hot to touch and become tender or swollen. In severe cases, blistering may occur.
To prevent sunburn, it’s important to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 on all exposed areas of your body before going outside. Wearing protective clothing like hats and sunglasses can also help shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
Sunburn Vs. Sun poisoning – Key differences
| Characteristic | Sunburn | Sun Poisoning (Severe Sunburn) |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Excessive exposure to UVB and UVA rays | Intense, prolonged UV radiation without adequate protection |
| Symptoms | Redness, pain, swelling, and, in some cases, blisters | Symptoms of sunburn, plus fever, chills, nausea, dizziness, and potential blistering and peeling of the skin |
| Severity | Mild to moderate discomfort, typically heals in a few days | More severe and systemic symptoms, potentially requiring medical attention |
| Systemic Effects | Generally limited to the skin | May lead to systemic effects like fever, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances |
| Long-term Effects | Can result in skin damage and an increased risk of skin cancer | May have more pronounced long-term effects due to the severity of the sunburn |
| Prevention | Sunscreen, protective clothing, shade, sunglasses, and hydration | Same preventive measures as for sunburn, but more critical to avoid intense and prolonged sun exposure |
| Treatment | Rest, aloe vera, over-the-counter pain relievers, and hydration | Medical attention may be required, and treatment may include intravenous fluids, pain management, and monitoring for complications |
Causes of Sunburn and Sun Poisoning
Sunburn and sun poisoning are both conditions that result from excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Here are the causes and differences between the two:
Sunburn
- Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to UV radiation, primarily UVB rays, for an extended period.
- UVB rays cause damage to the DNA in skin cells, which triggers inflammation as the body’s defense mechanism.
- Symptoms of sunburn include redness, pain, swelling, and sometimes blisters.
- Mild sunburn can be painful and uncomfortable but typically heals in a few days with proper care.
- Severe sunburn can lead to long-term skin damage, including premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Sun Poisoning (Severe Sunburn)
- Sun poisoning, also known as severe sunburn, is an extreme form of sunburn that is characterized by more severe and sometimes systemic symptoms.
- It can be caused by intense or prolonged exposure to UV radiation, often without adequate protection like sunscreen or clothing.
- In addition to the symptoms of sunburn, sun poisoning can include fever, chills, nausea, dizziness, and, in some cases, blistering, and peeling of the skin.
- Severe sunburn can result in dehydration and electrolyte imbalances due to the loss of fluids from blistering and damaged skin.
- Sun poisoning may also be more likely in individuals with fair skin, as they have less natural protection against UV radiation.
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding sunburn and sun poisoning. You can protect yourself by:
Applying Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF and reapply it regularly, especially after swimming or sweating.
Wearing Protective Clothing: Cover exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats.
Seeking Shade: Stay in the shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Using Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from UV radiation with sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays.
Hydrating: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as sun exposure can lead to dehydration.
Avoiding Tanning Beds: Tanning beds also expose the skin to harmful UV radiation and can lead to sunburn.
If you or someone you know experiences severe sunburn or sun poisoning, it’s essential to seek medical attention, as these conditions can have serious health consequences, including heatstroke, infection, and an increased risk of skin cancer in the long term.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Freepik
Image 1 By – Axelv, CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons








