Substance abuse refers to the excessive use or misuse of any substance, including alcohol and prescription medications. On the other hand, drug abuse specifically relates to the non-medical use of illicit drugs.
What is substance abuse?

(Image by macrovector on Freepik)
Substance abuse refers to the excessive and harmful use of substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, or illicit drugs. It goes beyond occasional or recreational use and becomes a pattern of behavior that negatively impacts an individual’s physical, mental, and social well-being.
At its core, substance abuse involves the misuse of substances for non-medical purposes. This can include using larger amounts than prescribed, taking medications not prescribed to you, or using illicit drugs recreationally. Substance abuse is characterized by a loss of control over drug consumption and an increasing tolerance towards the substance.
The effects of substance abuse can be wide-ranging. Physically, it can lead to deteriorating health conditions such as liver damage from excessive alcohol consumption or respiratory problems caused by smoking illicit substances. Mentally, substance abuse often leads to impaired judgment, memory loss, mood swings, and even mental health disorders like depression or anxiety.
Furthermore, substance abuse has significant social implications. Relationships may suffer as individuals prioritize their drug use over personal connections. Work performance may decline due to increased absenteeism or decreased productivity while under the influence.
It is important to note that substance abuse is a complex issue influenced by various factors including genetic predispositions, environmental influences (such as peer pressure), trauma history and underlying mental health conditions.
Identifying signs of substance abuse early on is crucial for effective intervention and treatment options tailored to each individual’s needs
What is drug abuse?
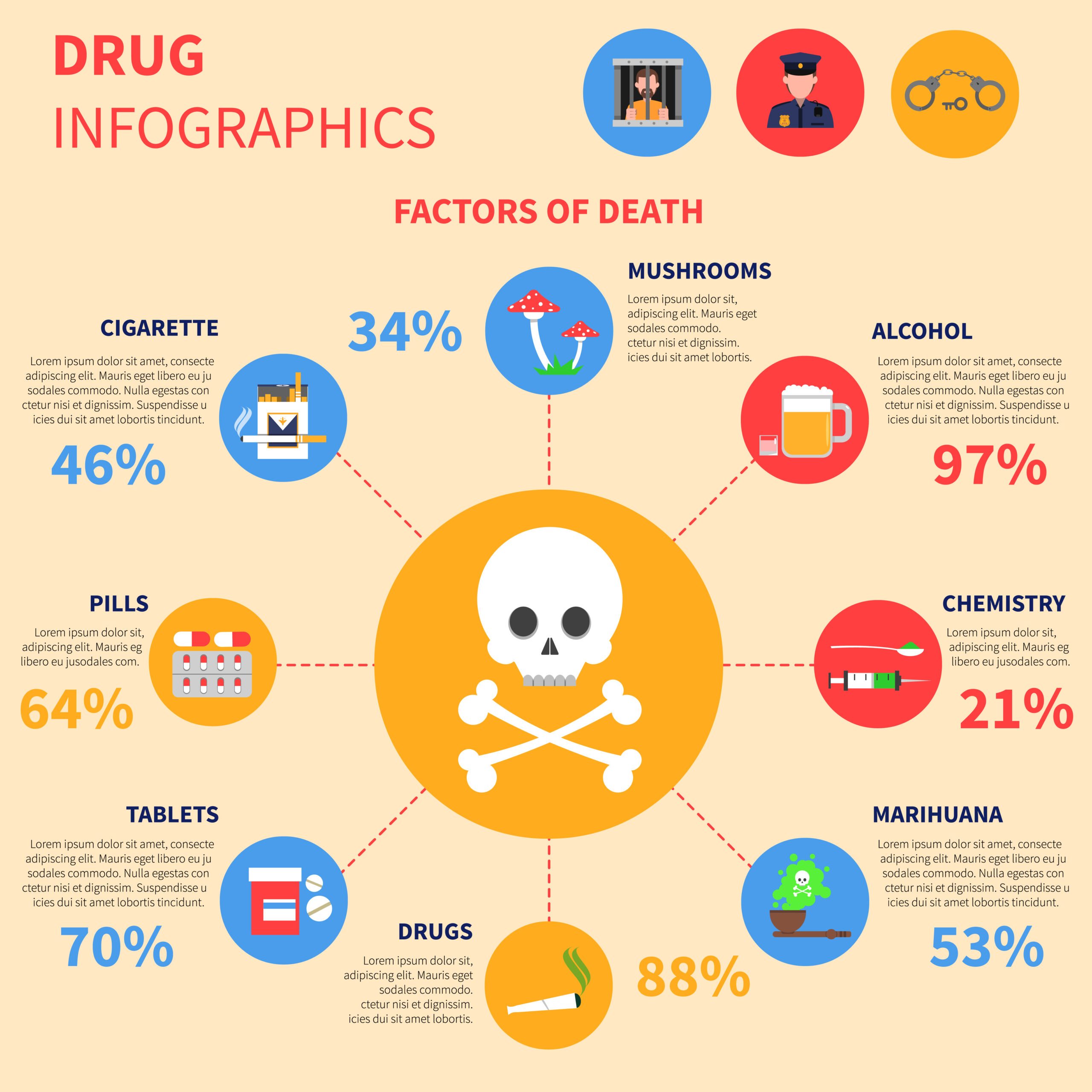
(Image by macrovector on Freepik)
Drug abuse refers to the misuse or excessive use of drugs, both legal and illegal, in a way that negatively impacts an individual’s physical and mental health. It involves taking substances with the intention of altering one’s mood, perception, or consciousness.
One key aspect of drug abuse is that it often involves the use of illicit substances such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, or marijuana. These drugs are highly addictive and can lead to severe health consequences.
Another form of drug abuse includes the misuse of prescription medications. This occurs when individuals take medication without a valid prescription or in higher doses than prescribed. Commonly abused prescription drugs include opioids (such as oxycodone), benzodiazepines (such as Xanax), and stimulants (such as Adderall).
The effects of drug abuse can be devastating on both personal and societal levels. Individuals who engage in drug abuse may experience physical health problems like organ damage or overdose. They may also suffer from mental health issues such as anxiety disorders or depression.
Additionally, drug abusers often face legal troubles due to their involvement in acquiring illicit substances or engaging in risky behaviors while under the influence.
It is important to note that not everyone who uses drugs becomes addicted; however, regular misuse significantly increases the risk for addiction and other negative outcomes.
Drug abuse is a serious issue that requires attention from individuals, communities, healthcare professionals, and policymakers alike. By understanding its complexities and promoting prevention efforts along with effective treatment options for those affected by it we can work towards reducing its impact on society
Substance abuse Vs. Drug abuse – Key differences
Substance abuse and drug abuse may sound like interchangeable terms, but they actually have distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial in order to address each issue effectively.
Substance abuse refers to the excessive or harmful use of any type of substance, including alcohol, prescription medications, and illicit drugs. This broad term encompasses a wide range of substances that can be abused. On the other hand, drug abuse specifically refers to the misuse or overuse of illegal drugs such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and marijuana.
While both involve harmful behavior and potential addiction, one key difference between substance abuse and drug abuse lies in their legality. Substance abuse covers legal substances like alcohol and prescription medications that are misused or taken excessively. Drug abuse solely relates to illegal substances that are used for non-medical purposes.
Another distinction is the societal perception surrounding these terms. Substance abuse tends to carry less stigma compared to drug abuse since it includes legal substances that can be prescribed by healthcare professionals for legitimate reasons. Drug abuse often implies engaging in criminal activities due to obtaining illegal drugs.
It’s important not only to understand the differences between substance abuse and drug use but also their respective signs and symptoms before seeking help or treatment options.
Signs and symptoms of substance abuse and drug abuse
Signs and symptoms of substance abuse and drug abuse can vary depending on the individual and the specific substances involved. However, there are some common indicators to look out for.
One of the key signs is a noticeable change in behavior. This could include sudden mood swings, increased aggression or irritability, and impaired judgment. Another red flag is a decline in personal hygiene or appearance. Individuals struggling with substance abuse may neglect their physical well-being as their focus shifts towards obtaining and using drugs.
Physical symptoms can also manifest themselves in various ways. These may include bloodshot eyes, dilated or constricted pupils, slurred speech, tremors, or unexplained weight loss/gain. Additionally, frequent illness or infections could be indicative of weakened immune function due to substance misuse.
Changes in social activities and relationships are often observed when someone is dealing with substance abuse issues. They may withdraw from previously enjoyed hobbies or abandon responsibilities at work or school. Strained relationships with family members and friends are not uncommon either.
Financial difficulties can arise as individuals prioritize purchasing drugs over meeting financial obligations such as paying bills or buying necessities like food. Legal troubles such as arrests for possession or driving under the influence may also occur.
It’s important to remember that these signs alone do not definitively indicate substance abuse; however, they should serve as warning signals that something is amiss. If you suspect someone you know may be struggling with substance abuse or drug addiction, it’s crucial to encourage them to seek professional help without judgment.
| Substance Abuse | Drug Abuse |
|---|---|
| Increased tolerance to a substance | Frequent cravings for drugs |
| Neglecting responsibilities and obligations | Using drugs despite negative consequences |
| Legal problems related to substance use | Engaging in risky behaviors to obtain drugs |
| Relationship issues and conflicts | Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not using drugs |
| Financial difficulties due to drug expenses | Failed attempts to quit or control drug use |
| Physical and psychological health problems | Deterioration in personal hygiene and appearance |
| Loss of interest in activities previously enjoyed | Social isolation and withdrawal from friends and family |
| Changes in sleep patterns and appetite | Drastic changes in mood and behavior |
| Secretive behavior and lying about substance use | Prioritizing drug use over other aspects of life |
| Loss of motivation and decreased productivity | Increased involvement in illegal activities to support drug habit |
Treatment options for substance abuse and drug abuse
Treatment options for substance abuse and drug abuse can vary depending on the individual’s needs and circumstances. It is important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to treating these issues.
One common treatment option is therapy, which can be incredibly beneficial in helping individuals address the underlying causes of their substance or drug abuse. This can include individual therapy, where a person works one-on-one with a therapist to explore their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors related to substance use.
Group therapy is another effective treatment option as it provides individuals with a supportive environment where they can share their experiences and learn from others who are going through similar struggles. Group sessions often involve discussions, activities, and exercises designed to promote insight and personal growth.
In some cases, medication may also play a role in the treatment of substance abuse or drug addiction. Medications can help manage withdrawal symptoms during detoxification or assist in reducing cravings for certain substances.
Additionally, holistic approaches such as yoga, mindfulness meditation, art therapy, and exercise have shown promise in supporting recovery efforts by promoting overall well-being and stress reduction.
It’s crucial to note that successful treatment requires ongoing support even after formal programs have ended. Aftercare programs like outpatient counseling or participation in support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide continued guidance and accountability for maintaining sobriety.
Finding the right combination of treatments tailored to an individual’s specific needs is essential for long-term recovery success.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Detoxification | The process of removing drugs from the body and managing withdrawal symptoms under medical supervision. |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation | Residential treatment where individuals live at a facility and receive intensive therapy, counseling, and support in a controlled environment. |
| Outpatient Rehabilitation | Non-residential treatment programs that provide counseling, therapy, and support while allowing individuals to continue living at home and attending work or school. |
| Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) | The use of medications, such as methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone, in combination with behavioral therapy to help manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms. |
| Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | A type of therapy that helps individuals identify and change unhealthy patterns of thinking and behavior related to substance abuse. |
| Group Therapy | Therapy sessions conducted in a group setting, allowing individuals to share experiences, receive support, and learn from others facing similar challenges. |
| Individual Counseling | One-on-one counseling sessions with a therapist or counselor to explore personal issues, develop coping strategies, and work towards recovery goals. |
| 12-Step Programs | Support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) that follow a 12-step recovery model, providing peer support and guidance in a structured format. |
| Holistic Approaches | Treatment approaches that address the individual's overall well-being, including physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects, through activities like yoga, meditation, and alternative therapies. |
| Aftercare and Relapse Prevention | Ongoing support and strategies to help individuals maintain sobriety after completing initial treatment, including follow-up counseling, support groups, and lifestyle adjustments. |
Prevention of substance abuse and drug abuse
Prevention of substance abuse and drug abuse is a crucial aspect that requires collective efforts from various stakeholders, including individuals, families, communities, schools, and governments. By implementing effective prevention strategies, we can reduce the occurrence and impact of these harmful behaviors.
Education plays a significant role in prevention. Schools should provide comprehensive drug education programs that equip students with knowledge about the risks associated with substance abuse and drug use. These programs should emphasize the importance of making healthy choices and developing strong refusal skills.
Parents also have an essential role to play in preventing substance abuse. Open communication within families creates a supportive environment where children feel comfortable discussing their concerns or temptations related to drugs or alcohol. Parents should be proactive in educating themselves about substances commonly abused by young people today and stay vigilant for signs of potential problems.
Community-based prevention initiatives are vital as well. These may include organizing awareness campaigns, promoting healthy alternatives such as sports or arts activities for youth, establishing neighborhood watch groups to deter illegal drug activity, providing access to treatment services when needed, and supporting law enforcement efforts.
Additionally, policymakers must focus on creating policies that restrict access to drugs through strict regulations surrounding prescription medications and controlled substances. They should also invest in evidence-based prevention programs aimed at high-risk populations such as adolescents who may be more susceptible to peer pressure.
Featured – Image By Freepik