im and iv (intravenous and intramuscular) injections are two common types of drug delivery methods. IM vs. IV have significant differences.
Intravenous Vs. Intramuscular injections – Key differences
(Stephen Andrews on Unsplash)
There are two main types of injections: intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM). Both are effective ways to deliver medication or fluids into the body, but they differ in how they work.
An IV injection is given directly into the bloodstream through a vein. This type of injection is the fastest way to get medication or fluids into the body because it bypasses the digestive system. IV injections are often used in emergencies when time is critical, such as when a person is having a heart attack or stroke.
Intramuscular (IM) injection is a type of needle injection that delivers medication directly into the muscles. Medication can be injected into the deltoid, gluteus, or quadriceps muscle groups. Intramuscular injections are used to deliver a wide variety of medications, including vaccines, analgesics, and even some antibiotics.
The IM route is generally faster than the IV route and allows for more precise dosing of medication. It also bypasses the digestive system, which can be important for medications that may be broken down or absorbed differently when taken orally.
One downside of IM injections is that they can be painful. To help reduce discomfort, many providers will use a smaller gauge needle or inject the medication slowly. Some medications may also need to be mixed with an anaesthetic before being injected to help further reduce pain.
IV therapy can be used for a variety of purposes, including hydration, administration of medications and blood products, and treatment of infections. IM injections are used to deliver medications that cannot be taken orally, such as certain types of antibiotics, hormones, and vitamins.
Which is better?
IV injections are generally faster-acting than IM injections since the medication goes directly into the bloodstream. This makes them ideal for emergencies where time is of the essence. However, they can be more difficult to administer, since they require a vein to be accessed. Additionally, IV injections carry a small risk of infection.
IM injections take a bit longer to take effect than IV injections since the medication has to be absorbed by the muscles before it enters the bloodstream. However, they are generally easier to administer than IV injections, since no vein is required. Additionally, IM injections carry a lower risk of infection than IV injections.
What happens if an intravenous injection is given intramuscularly?
If an intravenous (IV) injection is given intramuscularly (IM), the medication will not be absorbed as quickly. The IM route is slower than the IV route, so the medication will take longer to take effect. In addition, there is a risk of tissue damage and infection if the needle is not inserted correctly.
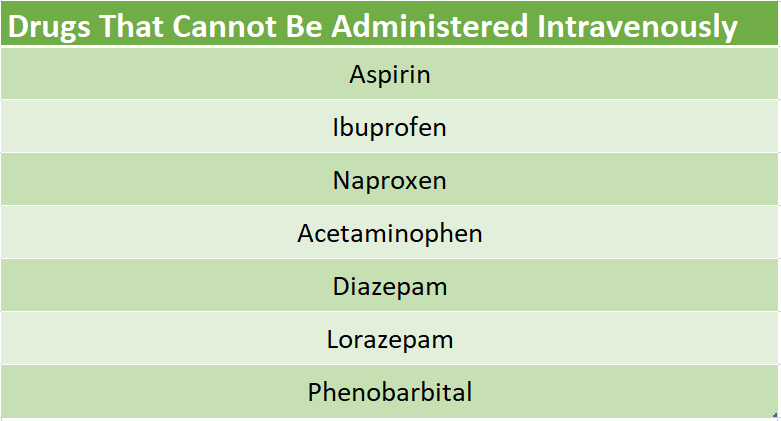
What drugs Cannot be given intravenously?
Many drugs cannot be given intravenously, including those that are not water-soluble and those that are too irritating to the veins. Some examples of drugs that cannot be given intravenously include:
What are the 3 locations for intramuscular injections?
There are three main locations for intramuscular injections:
- The Deltoid Muscle in the Arm
- The Gluteal Muscles in the Buttocks
- The Thigh Muscle.
The deltoid muscle is the most commonly used site for intramuscular injections in adults. It is a large muscle that is easy to access and provides good support for the needle.
The gluteal muscles are another common injection site, particularly for children and infants. They are located in the buttocks and provide good support for the needle.
The thigh muscle is also a common injection site, especially for larger doses of medication. It is a large muscle that can accommodate a longer needle, which is necessary for some types of injections.
Do you massage after the intramuscular injection?
There is no definitive answer to this question as everyone’s opinion will differ. However, some people believe that massaging the area after an intramuscular injection can help to disperse the medication and prevent it from being concentrated in one area. Others believe that massaging after an intramuscular injection can increase the risk of bruising or pain at the injection site. Ultimately, it is up to the individual to decide whether or not they want to massage the area after an intramuscular injection.
How long does the intramuscular injection take to work?
Intramuscular injections are generally faster-acting than oral medications or other types of less invasive delivery methods. In most cases, the medication will take effect within minutes. This is because the medication is directly injected into the muscle tissue, where it can be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. Additionally, intramuscular injections tend to have a higher bioavailability than other delivery methods, meaning that more of the medication reaches its target destination in the body.
What are the disadvantages of intravenous injection?
-The risk of infection is higher with IV injection than with other methods, such as intramuscular injection. This is because IV needles must be inserted directly into veins, which are located close to the surface of the skin. This increases the chances of bacteria contaminating the needle and entering the bloodstream.
-IV injections can be painful. The needle must be inserted into a vein, which can be difficult to find and may be located in a sensitive area, such as the hand or arm. Once inserted, the needle can cause discomfort or pain as fluid is injected into the vein.
-There is a risk of bruising or damage to blood vessels with IV injections. If the needle is not inserted correctly, it can damage delicate veins or cause bruising around the injection site.
-When you push IV meds too fast, they can go into your lungs instead of your bloodstream. This is called pulmonary edema, and it can be fatal.
What is the safest and easiest route of drug administration?
There are various routes of drug administration, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The safest and easiest route of drug administration is probably oral administration. This route avoids the risks associated with injecting drugs, such as infection, tissue damage, and blood clots. Oral administration is also less likely to cause an allergic reaction than other routes of administration.
Featured Image by – Diana Polekhina on Unsplash