Uranus has a much colder atmosphere (-224 degrees Celsius on average) than Neptune (-214 degrees Celsius on average). Additionally, Uranus has a rocky core, while Neptune does not. Uranus has 27 moons, while Neptune has 14.
What is Uranus?

Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is a gas giant planet that is about four times the diameter of Earth and is the third-largest planet in our solar system. Uranus is known for its distinctive blue-green color, which is caused by the presence of methane in its atmosphere.
Uranus was discovered in 1781 by the British astronomer William Herschel. It has a very low temperature and is classified as an ice giant, with a mostly hydrogen and helium atmosphere, along with traces of water, ammonia, and methane. Uranus has a highly tilted rotational axis, which is tilted at an angle of about 98 degrees relative to the plane of its orbit around the Sun, causing it to appear to roll along its orbit.
Uranus has 27 known natural satellites, the largest of which is named Titania. It also has a system of faint rings, discovered in 1977, which are composed of dust and small particles. Uranus has only been visited once by a spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1986, which provided valuable data about the planet and its moons.
What is Neptune?
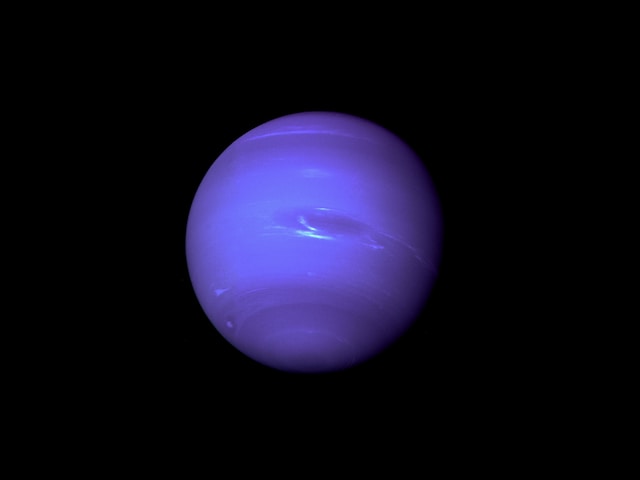
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the Solar System. In the Solar System, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times the mass of Earth and slightly larger in diameter. Neptune orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an average distance of 30.1 astronomical units (4.50×109 km). It completes one orbit around the Sun every 146 years and it has a rotational period of 16 hours 38 minutes as measured using Earth-based telescopes. This quick rotation gives Neptune’s atmosphere a blue appearance, similar to Uranus’.
Uranus Vs. Neptune – Key differences
Uranus and Neptune are both ice giants in our Solar System, and they share some similarities in terms of their composition and physical characteristics. However, there are some key differences between these two planets. Here are a few:
Size and mass: Neptune is slightly smaller than Uranus, with a diameter of about 30,600 miles (49,000 km) compared to Uranus’ diameter of about 31,500 miles (50,700 km). However, Neptune is more massive than Uranus, with a mass of about 17 Earth masses, while Uranus has a mass of about 14 Earth masses.
Color: Uranus has a distinctive blue-green color, while Neptune has a deeper blue color. The colors are caused by the presence of methane in their atmospheres, but the exact reason for the differences in color is not well understood.
Atmosphere: Both planets have similar compositions of hydrogen, helium, and methane, but the amount of methane in their atmospheres differs. Uranus has more methane than Neptune, which contributes to its blue-green color. Uranus’ atmosphere is also notable for its highly tilted axis, which causes extreme seasonal variations, while Neptune’s atmosphere has large, dark storm systems, including a famous one called the Great Dark Spot.
Rings: Both Uranus and Neptune have rings, but they differ in their characteristics. Uranus has a system of narrow, dark rings made of dust and small particles, while Neptune has a system of wider, brighter rings with more material, including ice particles.
Moons: Both planets have many moons, but Uranus has 27 known moons, while Neptune has 14. Uranus’ moons are mostly small and have unusual orbits, possibly due to past collisions or gravitational interactions with the planet’s rings. Neptune’s largest moon, Triton, is notable for its icy surface and geysers of nitrogen gas.
While Uranus and Neptune share some similarities as ice giant planets, they have distinct differences in their size, color, atmosphere, rings, and moons.
Interesting facts about Uranus and Neptune
- Uranus and Neptune are the two outermost planets in the solar system.
- They are often referred to as the “ice giants” because they are mostly made up of water, ice, and methane.
- Neptune is slightly larger than Uranus.
- Uranus has 27 moons, while Neptune has 14.
- Uranus’s atmosphere is made up of hydrogen, helium, and methane, while Neptune’s atmosphere is made up of hydrogen, helium, methane, and nitrogen.
- Uranus’s axis is tilted at an angle of 97 degrees, which means that it rotates on its side.
- Neptune was discovered in 1846 by Johann Galle, while Uranus was discovered in 1781 by William Herschel.
Why are Uranus and Neptune called twins?
Uranus and Neptune are sometimes referred to as “twins” because they are both classified as ice giant planets, and they share some similarities in their composition and physical characteristics. However, they are not identical and have some differences, as I mentioned in my previous response.
Both planets are primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with a significant amount of methane in their atmospheres, which gives them their distinctive blue-green and blue colors, respectively. They also have similar internal structures, with a rocky core surrounded by a thick layer of icy materials.
Uranus and Neptune also have comparable distances from the Sun, with Uranus being the seventh planet and Neptune being the eighth planet in our Solar System. They are also relatively close in size, with Uranus being slightly larger in diameter, but Neptune being more massive.
Despite these similarities, there are still differences between Uranus and Neptune, such as their ring systems, atmospheres, and moons. Therefore, while they are sometimes called “twins,” they are not identical and have unique features that make them distinct from one another.
Why Uranus is blue?
Uranus appears blue in color because of the presence of methane in its atmosphere. Methane is a greenhouse gas that absorbs red light and reflects blue light, giving Uranus its distinctive blue-green hue.
The upper atmosphere of Uranus consists mostly of hydrogen and helium with traces of methane, which is only about 2.3% of the total atmospheric composition. The methane molecules in the atmosphere scatter the blue light, while absorbing the red light, giving Uranus its blue-green color.
Another contributing factor to the blue color of Uranus is the fact that the planet has a highly tilted axis of rotation. Uranus’ axis is tilted at an angle of about 98 degrees relative to the plane of its orbit around the Sun, which causes the planet to appear to roll along its orbit. This results in extreme seasonal variations in which one hemisphere is bathed in sunlight for many years while the other experiences long periods of darkness. The seasonal variations can affect the distribution of clouds and hazes in Uranus’ atmosphere, which could also impact the planet’s color.
Overall, the blue color of Uranus is caused by the presence of methane in its atmosphere, which scatters blue light and reflects it back to space, making the planet appear blue-green from a distance.
Featured Image By – WikiImages from Pixabay









