Traits refer to observable characteristics or behaviors of an organism, genes are the specific segments of DNA that determine these traits.
What is a trait?
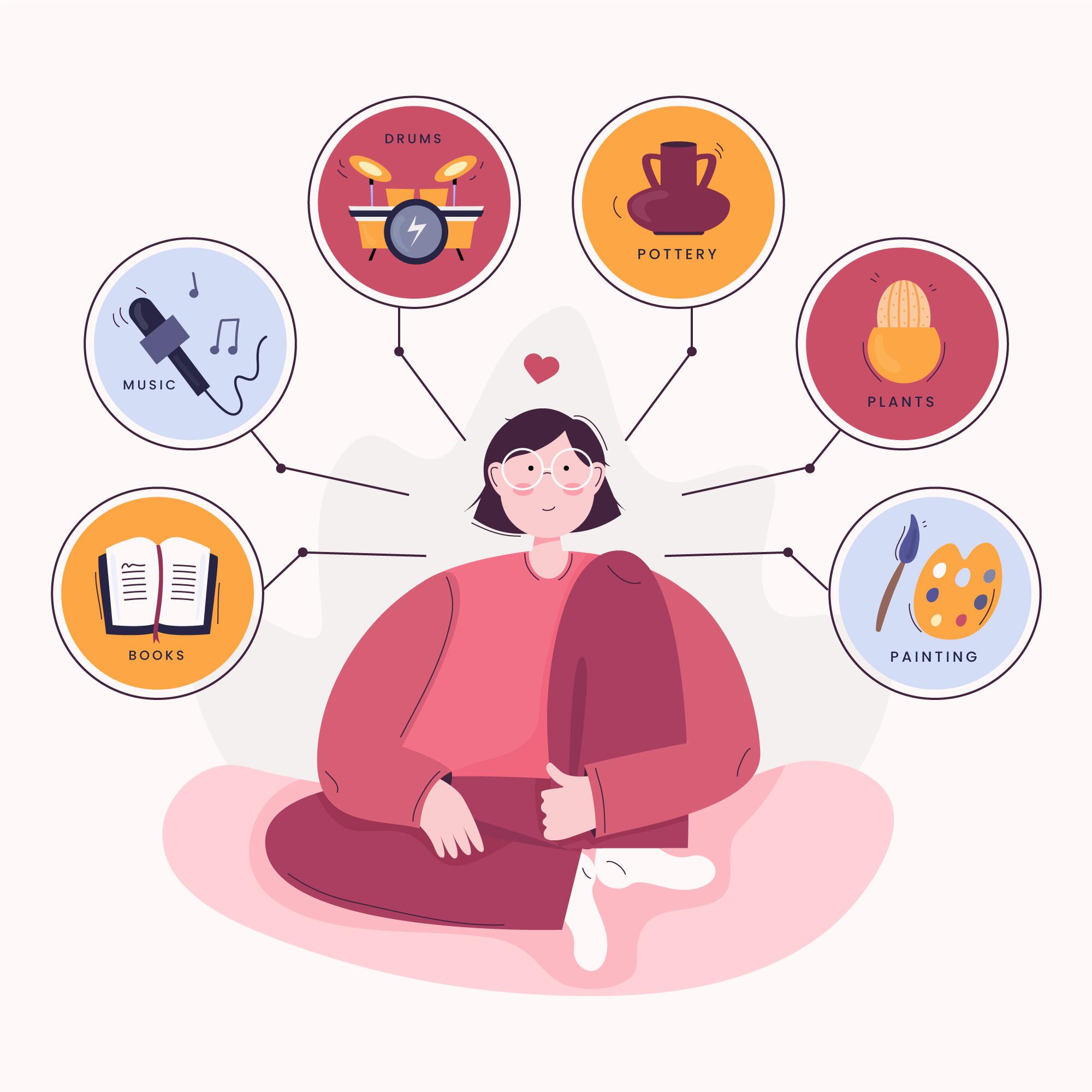
Traits as the observable characteristics that make each individual unique. They are the outward manifestations of our genetic makeup and can include physical features like eye color, hair texture, or height. But traits go beyond just appearances – they also encompass behavioral patterns and personality traits.
Traits are influenced by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Our genes provide the blueprint for these traits, but how they actually manifest in an individual can be shaped by various external factors such as upbringing, nutrition, and lifestyle choices.
Traits play a significant role in shaping who we are as individuals. They reflect both our genetic heritage and the experiences that shape us throughout our lives. So next time you look in the mirror or notice someone’s distinctive behavior, remember that behind every trait lies an intricate web of genetic information waiting to be unraveled!
What is a gene?

A gene is simply a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building and maintaining our bodies.
Genes act as blueprints for specific traits or characteristics, such as eye color, height, or even predispositions to certain diseases. They provide the code necessary to produce proteins, which carry out essential functions in our cells.
But genes don’t work alone – they interact with each other and with the environment to determine how these traits manifest in an individual. This complex dance between genes and their surroundings is known as gene expression.
Mutations can occur within genes, altering their instructions and potentially leading to variations in traits or even health conditions. Sometimes these mutations can be beneficial, providing an advantage in certain environments. Other times, they may have negative consequences.
Trait Vs. Gene – Key differences
| Trait | Gene |
|---|---|
| A trait refers to a specific characteristic or feature of an organism, such as eye color, height, or behavior. | A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for building and functioning of a specific protein or RNA molecule. |
| Traits are the observable or measurable expressions of genes. | Genes are the hereditary units that determine traits. |
| Traits can be influenced by multiple genes as well as environmental factors. | Genes are the fundamental units of heredity and are passed down from parents to offspring. |
| Traits can vary within a population and can be influenced by genetic and environmental interactions. | Genes are the specific sequences of DNA that provide instructions for the synthesis of proteins or RNA molecules. |
| Traits can be influenced by factors such as genetic variations, mutations, and environmental influences. | Genes can undergo mutations, which can alter their structure and function, potentially leading to changes in traits. |
| Traits can be observed and studied directly through physical or behavioral characteristics. | Genes are studied indirectly through techniques such as DNA sequencing, genetic mapping, and genetic engineering. |
| Examples of traits include eye color, hair type, height, and intelligence. | Examples of genes include the BRCA1 gene associated with breast cancer, the CFTR gene associated with cystic fibrosis, and the ABO gene associated with blood type. |
How do traits and genes interact?
The interaction between genes and traits is complex and multifaceted. Some traits may be controlled by just one gene (monogenic), while others may involve multiple genes (polygenic). In addition to this genetic influence, external factors such as diet, lifestyle choices, and even stress can modify gene expression and impact trait development.
Furthermore, genetic variations within populations contribute to individual differences in trait expression. These variations occur through random mutations or recombination during reproduction.
Understanding how genes and traits interact is crucial for fields like genetics research and personalized medicine. By unraveling these interactions, scientists aim to better understand disease risk factors and develop targeted therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
What are some examples of traits and genes?
Eye Color:
Trait: Eye color refers to the color of an individual’s iris, such as blue, brown, green, or gray.
Gene: Multiple genes contribute to eye color, including OCA2, HERC2, and TYR.
Blood Type:
Trait: Blood type categorizes an individual’s blood into different types, such as A, B, AB, or O.
Gene: The ABO gene determines the presence of A, B, or O antigens on red blood cells.
Height:
Trait: Height refers to the vertical stature of an individual.
Gene: Various genes influence height, including the HMGA2, GDF5, and EFEMP1 genes.
Hair Texture:
Trait: Hair texture describes the physical characteristics of an individual’s hair, such as straight, curly, or wavy.
Gene: The TCHH gene, among others, plays a role in determining hair texture.
Taste Sensitivity:
Trait: Taste sensitivity refers to an individual’s ability to perceive different tastes, such as sweet, salty, bitter, or sour.
Gene: The TAS2R38 gene is associated with the ability to taste bitterness, including compounds like PTC (phenylthiocarbamide) and PROP (propylthiouracil).
Image Credits
Featured Image By – Freepik
Image 1 By – Freepik
Image 2 By – brgfx on Freepik