Blue cheese is a broad term, while Gorgonzola is a specific type with a milder taste and creamier texture. Both offer unique flavors and culinary versatility.
TL;DR Blue Cheese Vs. Gorgonzola
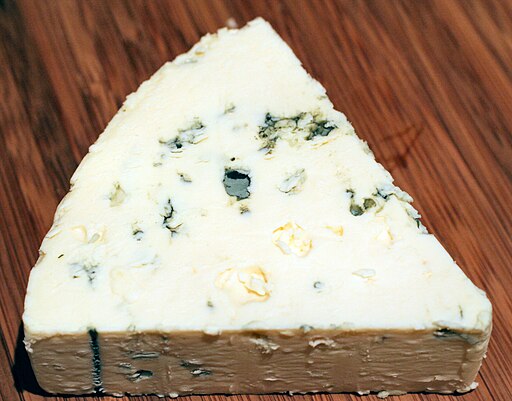
Blue Cheese and Gorgonzola, both types of blue-veined cheeses, have distinct differences. Blue cheese, a broad term, often has a stronger, tangier taste and crumbly texture. Gorgonzola, originating in Italy, is milder and creamier, with variations like Dolce and Piccante.
Both offer health benefits like calcium, protein, and probiotics. Culinary uses include salads, pasta, meats, and desserts. Choosing between them depends on personal taste preferences, intensity, culinary applications, and pairing preferences. Conducting a taste test and considering how you plan to use the cheese can help make the decision. Ultimately, both cheeses add richness and flavor to various dishes.
Blue Cheese

Blue cheese is a diverse category of cheeses characterized by distinctive blue veins. Made by introducing Penicillium mold, it undergoes aging to develop complex flavors. Varieties like Roquefort, Stilton, and Gorgonzola showcase diverse textures, from crumbly to creamy.
Bold and tangy, blue cheese enhances salads, dressings, sauces, and pairs superbly with fruits or meats. Rich in calcium and protein, it provides nutritional benefits while its unique taste adds depth to various culinary creations. Whether crumbled on a salad or melted into a sauce, blue cheese remains a beloved choice for those seeking robust and savory flavors.
Gorgonzola

Gorgonzola, an Italian blue cheese, boasts a rich history and distinct flavors. Originating from the town of Gorgonzola, it comes in two types: Dolce and Piccante. Dolce offers a milder, creamier taste, while Piccante presents a sharper flavor. Recognizable by its marbled appearance,
Gorgonzola complements salads, pastas, and meats. With a shorter aging period than other blues, it appeals to a broader audience. Packed with calcium and protein, Gorgonzola contributes to a balanced diet. Whether crumbled on a pizza or paired with fruits, this cheese provides a delightful culinary experience for those exploring diverse and flavorful options.
Blue Cheese Vs. Gorgonzola – Key differences

Culinary Uses of Blue Cheese and Gorgonzola
Culinary Uses of Blue Cheese
- Salads: Crumble blue cheese over salads for a burst of bold flavor, balancing well with greens, fruits, and nuts.
- Dressings: Create creamy blue cheese dressings for salads or dipping sauces, adding depth to the taste.
- Sauces: Melt into rich sauces for pasta, steaks, or burgers, enhancing the overall umami and creaminess.
- Appetizers: Serve on cheese boards or alongside fruits, crackers, and honey for a delightful appetizer.
- Burgers: Elevate burgers by topping them with melted blue cheese, providing a savory and tangy kick.
- Pizza: Sprinkle crumbled blue cheese on pizza for a gourmet twist, especially with figs or prosciutto.
Culinary Uses of Gorgonzola
- Pasta: Melt Gorgonzola into pasta dishes like gnocchi or risotto, creating a creamy and flavorful sauce.
- Salads: Crumble Gorgonzola over salads, offering a creamy texture and balancing well with fruits or balsamic glaze.
- Appetizers: Serve Gorgonzola with crackers, figs, or honey as part of an elegant appetizer spread.
- Cheese Boards: Pair Gorgonzola with other cheeses, nuts, and dried fruits for a sophisticated cheese board.
- Meat Pairings: Complement meats like steak or pork with melted Gorgonzola, adding richness to the dish.
- Desserts: Experiment with sweet and savory by incorporating Gorgonzola into desserts like tarts or cheesecakes.
Health Benefits of Blue Cheese and Gorgonzola
Health Benefits of Blue Cheese
- Calcium Source: Blue cheese is rich in calcium, supporting bone health, muscle function, and nerve transmission.
- Protein Content: It provides protein essential for tissue repair and muscle development.
- Moderate Calories: Compared to some cheeses, blue cheese is relatively low in calories, suitable for calorie-conscious individuals.
- Probiotic Potential: Fermentation in blue cheese may introduce beneficial bacteria, promoting gut health.
- Antioxidants: Contains antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Potential Anti-Inflammatory: Studies suggest moderate consumption may have anti-inflammatory effects.
Health Benefits of Gorgonzola
- Calcium and Protein: Like blue cheese, Gorgonzola contributes to calcium intake for bone health and provides protein.
- Beneficial Bacteria: As a fermented cheese, Gorgonzola contains probiotics supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
- Moderate Calories: With mindful portions, it can be part of a balanced diet without excessive calorie intake.
- Heart-Healthy Fats: The fats in Gorgonzola are primarily monounsaturated, associated with heart health.
- Nutrient Diversity: Offers essential nutrients in a flavorful package, encouraging varied nutrient intake.
- Versatile Culinary Use: Incorporating Gorgonzola into dishes enhances flavors, encouraging enjoyable and nutritious meals.
Image Credits
Featured Image By – No machine-readable author provided. Brookie assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 1 By – Peachyeung316, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 2 By – Ramagliolo9, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons