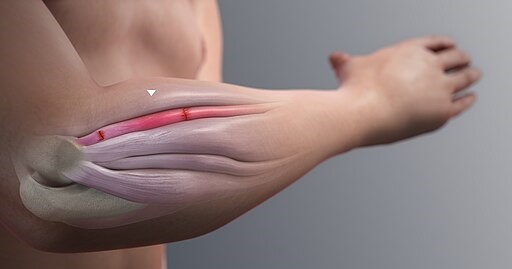
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) is pain on the outer elbow, while golf elbow (medial epicondylitis) is pain on the inner elbow.
TL;DR Tennis elbow Vs. Gold elbow
The main difference between tennis elbow and golf elbow lies in their location – one affects the outer part of the joint while the other affects the inner part. Additionally, tennis elbow tends to arise from movements involving wrist extension and gripping activities whereas golfers frequently experience medial epicondylitis due to forceful flexion of their wrists during impact.
What is tennis elbow?

Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the tendons on the outer side of the elbow. Despite its name, tennis players aren’t the only ones susceptible to this pesky ailment. It can affect anyone who performs repetitive gripping or wrist extension motions.
The primary cause of tennis elbow is overuse and strain on the tendons that connect your forearm muscles to your humerus bone. This constant stress leads to tiny tears in these tendons, resulting in pain and discomfort.
Typically, tennis elbow gradually develops over time rather than being an acute injury. Activities such as playing tennis (hence the name), painting, gardening, or even using a computer mouse excessively can contribute to its onset.
Symptoms of tennis elbow include pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow that may radiate down into your forearm. You may also experience weakness in your grip strength or difficulty holding objects like cups or utensils.
Early intervention through rest, ice application, physical therapy exercises focused on strengthening and stretching, along with anti-inflammatory medications are often recommended for managing tennis elbow symptoms. In severe cases where conservative treatments don’t provide relief, corticosteroid injections or surgery might be considered as options by healthcare professionals.
What is golf elbow?
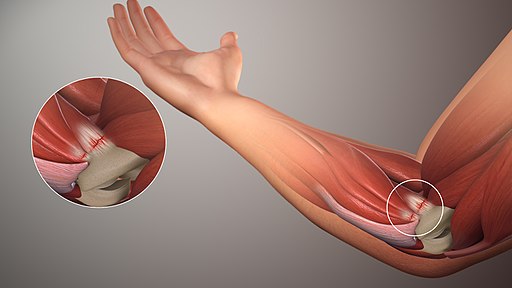
Golf elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that affects the inner side of the elbow. While it shares similarities with tennis elbow, there are some key differences to note.
One of the main causes of golf elbow is repetitive wrist and forearm movements, particularly those involved in gripping or swinging motions. This can occur not only during golf swings but also in other activities such as gardening or painting.
The primary symptom of golf elbow is pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow. This discomfort may radiate down to the forearm and wrist. It can be exacerbated by activities that involve gripping objects or bending the wrist.
Unlike tennis elbow, which primarily affects the outer part of the arm near the bony prominence called lateral epicondyle, golfers typically experience pain on the inside portion near a similar protrusion called medial epicondyle.
Diagnosing golf elbow involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional who will assess your symptoms and medical history. In some cases, imaging tests like an MRI or X-ray may be recommended to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for golf elbow often includes rest, ice therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, and physical therapy exercises focused on stretching and strengthening muscles in the affected area. In more severe cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be considered.
Tennis elbow Vs. Gold elbow – Key differences
| Characteristic | Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) | Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis) |
|---|---|---|
| Location of Pain | Outer part of the elbow (lateral epicondyle) | Inner part of the elbow (medial epicondyle) |
| Common Activities | Repetitive wrist and forearm movements, such as gripping and wrist extension | Repetitive wrist flexion and gripping activities, often seen in golf and racquet sports |
| Pain Aggravation | Aggravated by gripping objects, especially with the backhand in tennis | Exacerbated by activities like golf swings, lifting, and throwing |
| Specific Muscles | Affects the extensor muscles of the forearm | Impacts the flexor muscles of the forearm |
| Typical Symptoms | Pain and tenderness on the outer elbow, weakness in the affected arm | Pain and tenderness on the inner elbow, weakness and stiffness in the forearm |
| Onset and Progression | Often develops gradually and can become chronic | Can develop gradually but may also result from a sudden injury |
| Diagnostic Tests | Diagnosed through clinical examination and medical history | Diagnosed through clinical examination, imaging (e.g., ultrasound), and medical history |
| Treatment Approach | Rest, ice, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes bracing or injections | Rest, ice, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and, in some cases, bracing or injections |
| Preventive Measures | Proper technique, equipment adjustment, and strengthening exercises | Proper technique, warm-up routines, and strength training |
| Prognosis | Recovery can vary, but most cases improve with conservative treatment | Recovery duration varies, and some cases may require more prolonged treatment or even surgery |
Image Credits
Featured Image By – www.scientificanimations.com, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Image 1 By – Sgdp, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Image 2 By – www.scientificanimations.com, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons