Desk research is generally quicker, cheaper, and easier to manage than field research, but it can also be less reliable due to its reliance on secondary sources. On the other hand, field research often provides more accurate results but requires more time and resources in order to conduct effectively.
Desk Research
(Photo by Firmbee.com on Unsplash )

Desk research is conducted at a desk, usually in an office or library, and usually entails the use of secondary sources. This type of research is typically used to gather information that is already available, such as data from government reports, journal articles, books, and other published materials.
Field Research
(Image by federiconmunoz from Pixabay )

Field research is a type of research that is conducted in order to collect data directly from individuals, rather than relying on data that has already been collected. This allows for a more personal and in-depth understanding of the topic being studied. Field research is often used in social sciences such as anthropology and sociology, but can be used in any discipline where firsthand information is desired.
There are many different types of field research, but all share the common goal of collecting primary data. Some common methods of field research include interviews, focus groups, and participant observation. Data collected through field research is usually qualitative in nature, as it provides detailed insights into people’s thoughts and behaviors. However, quantitative data can also be collected through certain methods such as surveys.
Conducting field research can be challenging, as it requires careful planning and execution. Researchers must often gain access to people and places that are not easy to reach, and they must be prepared to deal with unexpected situations. Despite these challenges, field research provides an invaluable opportunity to collect rich and nuanced data that cannot be obtained through other methods.
Pros and Cons of each method
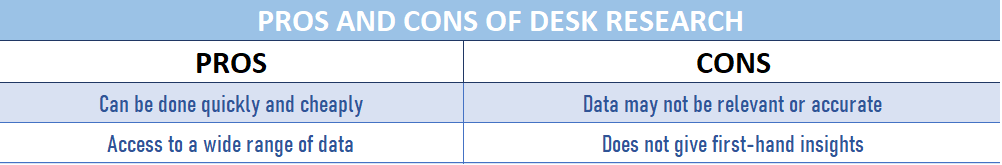
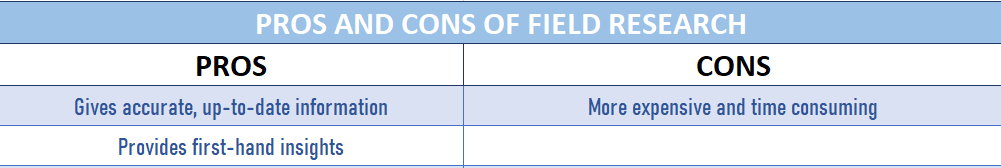
There are a few key differences between desk research and field research. Desk research is conducted using data that already exists, while field research involves going out and collecting primary data. Desk research is usually cheaper and quicker to conduct than field research, but it can be less reliable because the data may not be relevant to the current situation. Field research is more expensive and time-consuming, but it gives you accurate, up-to-date information.
When to use each method
There are benefits and drawbacks to both desk research and field research. The main difference is that desk research is conducted using secondary data, while field research is conducted using primary data.
Secondary data is data that has already been collected and published by someone else, such as government statistics, industry reports, or news articles. This type of research is typically quicker and cheaper than field research, since the data has already been gathered. However, it can be less reliable than field research, since you are relying on someone else’s interpretation of the data.
Primary data is data that you collect yourself through interviews, surveys, focus groups, or observations. This type of research is generally more reliable than desk research, since you are collecting the data directly yourself. However, it can be more expensive and time-consuming to collect primary data yourself.
How to combine both methods for the best results
If you’re looking to get the most accurate and complete research results possible, it’s best to use a combination of both desk research and field research methods. Desk research can give you an overview of a topic, while field research can provide more detailed and specific information.
Here’s how to combine both methods for the best results:
- Start with desk research to get an overview of your topic. This can include things like reading articles, watching videos, and searching online.
- Once you have a good understanding of the general topic, you can then move on to field research to get more specific information. This can involve things like conducting interviews or surveys, observing people in naturalistic settings, or doing experiments.
- Finally, compare and contrast the information you’ve gathered from both desk research and field research to get a well-rounded understanding of your topic.
What is an example of desk research?
One of the most common is through online research. This can involve anything from reading articles and blog posts to watching videos and conducting interviews via email or social media.
Another way to conduct desk research is through more traditional means, such as visiting a library or searching through archives. This can be helpful if you’re looking for specific information that might not be readily available online.
What are some methods of field research?
Participant observation is a method of field research in which the researcher immerses themselves in the everyday lives of the people they are studying. This involves spending time with people in their natural environment, observing them as they go about their daily activities. Participant observation can be either structured or unstructured; in structured participant observation, the researcher has a set plan for what they want to observe, while in unstructured participant observation, the researcher simply observes and records what they see without preconceived notions about what they will find.
Ethnography is another common method of field research. Ethnography is defined as “the systematic study of people and cultures” (Kottak, 2005). Ethnographers typically spend extended periods of time living with the people they are studying, in order to fully understand their way of life. This type of research is often used to study cultures that are different from our own, or that we have limited access to.
Case study is a third method of field research that involves an intensive investigation of a single individual or group. Case studies are often used to investigate rare or atypical phenomena. The goal of case study research is to describe in depth
What are some examples of field research?
Field research is a type of research that is conducted in natural settings. This means that the researcher goes to the site where the phenomenon under study occurs. Field research can be conducted in a variety of settings, including businesses, schools, and homes.
Some examples of field research include:
- Observing people in their natural environment (e.g., watching customers shop in a store)
- Conducting interviews with people in their natural environment (e.g., asking people about their shopping habits while they are waiting in line at a store)
- Participating in activities with people in their natural environment (e.g., joining a book club or attending a religious service)
- Keeping a field diary or journal (e.g., recording observations about people’s behavior during the day)
What are sources of desk research?
There are a number of sources of desk research, which can be broadly divided into two categories: Primary sources and Secondary sources.
Primary sources are data that are collected firsthand by the researcher, such as surveys, interviews, and observations. This type of data is considered to be more reliable than secondary sources, which are data that have been collected by someone else and may be less accurate or complete.
Secondary sources include things like newspapers, magazines, websites, books, and reports. This type of data can be useful for getting an overview of a topic or for finding specific information, but it is important to remember that it may not be as reliable as primary sources.
What are the steps in field research?
Field research is a type of data gathering that involves going out into the field to collect first-hand information. This can be done through interviews, focus groups, observations, or surveys. It is usually used to gather information on a specific target audience or market.
There are four main steps in field research:
- Define the research objectives – what are you trying to learn?
- Develop a research plan – how will you collect the data?
- Collect the data – this is where you go out into the field and gather the information you need.
- Analyze the data – once you have all of your data, it’s time to sit down and make sense of it all.
How do you structure a desk research?
When conducting desk research, also known as secondary research, you are primarily relying on already existing data. This could be in the form of market reports, government statistics, articles, etc. The goal is to collect as much relevant information as possible to help you answer your research question.
To structure your desk research effectively, start by clearly defining your research question. Once you have a good understanding of what you want to know, you can begin searching for relevant data sources. Try to use a variety of sources to get a well-rounded view of your topic. When evaluating each source, consider its reliability, relevance, and timeliness.
Once you have collected all of your data, it’s time to start organizing it. A good way to do this is to create a table with three columns: key findings, evidence from sources, and implications/relevance to your research question. This will help you keep track of the most important information and see how it all fits together. Desk research can be a lot of work, but by taking the time to do it carefully, you’ll end up with high-quality information that can be used to make sound decisions.
What type of research is best for young kids?
One type of research is desk research, which is conducted using existing data sources such as books, articles, and reports. Desk research is great for getting an overview of a topic, and can be done relatively quickly.
Another type of research is field research, which involves collecting data through direct observation and interaction with people. Field research can be more time-consuming than desk research, but it can provide insights that desk research might miss.
Which type of research is best for young kids will depend on the particular project and what information is needed. However, both desk and field research have value and can provide useful insights.
What type of research is best for college students?
That depends on the topic and the student’s goals. If a student wants to learn about a topic that can be researched using only library resources, then desk research is the way to go. However, if a student wants to learn about a topic that requires data collection in the field, then field research is necessary.
Both desk research and field research have their advantages and disadvantages. Desk research is less time-consuming and can be done from anywhere with an internet connection. Field research, on the other hand, allows students to get first-hand experience with their topic of choice.
Ultimately, it’s up to the student to decide which type of research is best for them. If you’re unsure of which type of research to use for your project, talk to your professor or a librarian for guidance.
What are the 4 types of research methods?
There are four main types of research methods: Desk research, Field research, Surveys, and Experiments.
Desk research is the process of gathering data from existing sources, such as books, articles, reports, and other primary and secondary sources. This type of research is often used to gain an understanding of a topic or issue before conducting further research.
Field research involves collecting data directly from individuals through interviews, focus groups, or observations. This type of research allows for a more in-depth understanding of a topic or issue than desk research alone.
Surveys are a type of research that involve collecting data from a large group of people through questionnaires or interviews. This method is often used to gather general information about people’s opinions or behaviors on a particular issue.
Experiments are a type of research that test how well something works under specific conditions. This method is often used in the sciences to test hypotheses and gather data about cause-and-effect relationships.
Featured Image By – Photo by UX Indonesia on Unsplash








