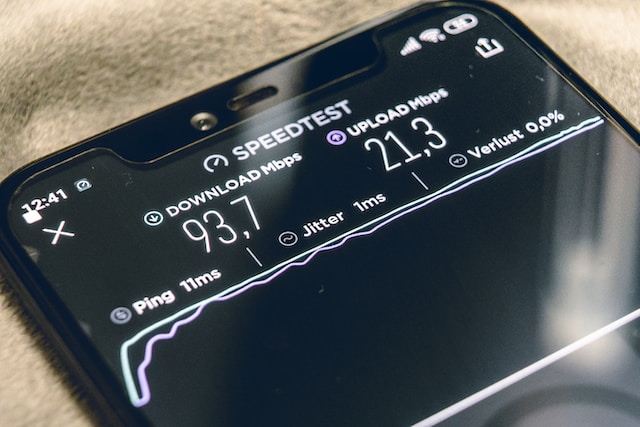
Jitter and latency are two crucial factors that affect the performance of networks. Jitter is the variation in delay between packets while latency is the time taken for a packet to travel from source to destination. Both can cause disruptions in network communication resulting in slow or interrupted transmission.
What is jitter?
(Image by Emilian Robert Vicol from Pixabay )
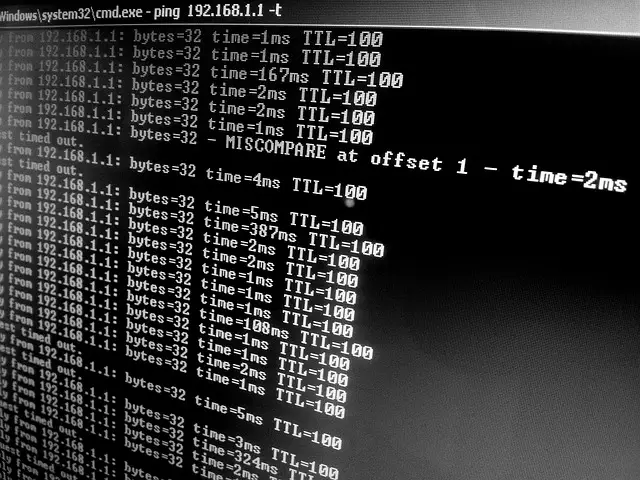
Jitter refers to the variation in time between packets that are sent and received over a network. In other words, it is the difference between when a packet was expected to arrive and when it actually arrived. Jitter can be caused by several factors including congestion on the network, hardware issues or software problems.
Jitter can cause delays in voice and video calls which result in poor quality connections. If you hear someone’s voice breaking up during a call or see pixelated images while streaming online, then there’s probably some jitter happening on your network.
To measure jitter accurately, you need to calculate the average amount of deviation from an ideal timeline for all packets delivered during a specific period. The higher this deviation is, the more significant the jitter will impact performance.
Reducing jitter often involves implementing Quality of Service (QoS) rules that prioritize traffic based on types of data being transmitted. For example, QoS could ensure that video streams receive priority over regular web browsing traffic.
Understanding what causes jitter and how to reduce its impact is essential for ensuring smooth network performance with clear audio and video quality during online activities such as gaming and streaming media content.
What is latency?
(Photo by thiago japyassu)
Latency is a term that describes the amount of time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. In other words, it’s the delay between when a message or request is sent and when it is received.
Latency can be influenced by several factors such as network congestion, routing issues, and distance between devices. The longer the distance data has to travel, the higher the latency will be.
One common example of latency in action is online gaming. In this scenario, players need instant feedback on their actions in order to operate effectively within virtual environments. High latencies can lead to slow response times which make gameplay difficult if not impossible.
For businesses and organizations relying on real-time applications like video conferencing or VoIP services high latencies can result in poor voice quality or dropped calls.
Several methods exist today for reducing latency including load balancing across multiple servers and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) designed specifically for improving performance.
Jitter Vs. Latency – Key differences
Jitter and latency are both related to network performance, but they refer to different aspects of network performance. Here are the key differences between the two:
Definition:
Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point in a network to another. It’s the delay that occurs between the time a request is made and the time the response is received.
Jitter is the variation in the delay of packet delivery over a network. It’s the deviation from the expected or average delay.
Cause:
Latency is caused by the distance between the source and destination, the number of hops the packet must make, and the congestion on the network.
Jitter is caused by congestion on the network, variations in the processing time of network devices, and other factors that can cause delays.
Measurement:
Latency is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) and is often expressed as round-trip time (RTT), which is the time it takes for a packet to be sent from the source to the destination and back again.
Jitter is typically measured in microseconds (μs) and is calculated by measuring the variance of the delay between packets.
Impact:
Latency can impact real-time applications such as online gaming, video conferencing, and voice over IP (VoIP), causing lag and delays in communication.
Jitter can impact real-time applications as well, causing audio and video distortion, dropped packets, and other issues that can negatively impact network performance.
Latency and jitter are both important metrics for assessing network performance, they refer to different aspects of network behavior. Latency refers to the delay between sending and receiving data, while jitter refers to the variation in delay over time. Understanding these differences can help network administrators diagnose and troubleshoot network issues more effectively.
How to improve jitter and latency
Improving jitter and latency can greatly enhance the performance of your network. Here are some tips to help you achieve this:
- Optimize Your Network Configuration: Ensure that your routers, switches, and other networking devices are properly configured. Check for firmware updates from your vendors and apply them as needed.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) Settings: Prioritize traffic on your network by configuring QoS settings to give priority to critical applications such as VoIP or video streaming.
- Monitor Network Performance Regularly: Keep an eye on the performance of your network by monitoring key metrics like packet loss rate, throughput, jitter, and latency.
- Upgrade Your Hardware: If you’re still using outdated hardware that is not capable of handling high-speed data transfers or has limited processing power/memory capacity, consider upgrading to newer equipment.
- Implement Traffic Shaping Techniques: Use traffic shaping techniques such as buffering or queuing algorithms in order to manage traffic flows effectively based on their importance level.
What is Ping?
Ping is a term used to measure the latency or delay of a network connection. It sends small packets of data from your device to another and measures the time it takes for them to be returned. Ping is measured in milliseconds (ms), with lower values indicating faster response times.
A low ping means that there is minimal delay between your device and the server, which results in smoother online experiences such as gaming, video calls, and streaming. On the other hand, a high ping may result in lagging, buffering, or even disconnections.
Ping time can vary depending on factors such as distance between devices, internet speed and quality of service provided by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Therefore, it’s important to regularly check your ping time especially if you’re experiencing connectivity issues.
Understanding what ping is and how it affects your network performance can help you troubleshoot any problems that arise while using online services.
What is throughput?
Throughput is the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given time. It refers to the speed at which data is transferred from one point to another. Unlike latency and jitter, throughput measures the actual amount of data that reaches its destination within a specific timeframe.
Throughput is an essential metric for measuring network performance because it determines how much bandwidth you have available for your applications. A high throughput means that more data can be sent and received quickly, resulting in faster communication between devices.
Several factors affect throughput, including network congestion, packet loss, and quality of service (QoS) settings. To optimize your network’s throughput, it’s crucial to prioritize traffic based on their importance and allocate sufficient bandwidth to each application.
Understanding throughput is critical for businesses and individuals who rely on fast and reliable internet connections. By monitoring this metric regularly, you can identify any issues with your network’s performance promptly and take corrective action before they impact productivity or user experience.
Can jitter be higher than latency?
The answer is yes. Jitter values represent fluctuations above and below the average latency value which means that if you have high levels of jitter then you will also have high levels of latency but not necessarily vice versa.
Therefore, it’s crucially important to monitor both metrics regularly so that you can identify any potential issues with your network connectivity before they become bigger problems affecting user experience.
How do you calculate latency and jitter?
Calculating latency and jitter is an important step in understanding your network’s performance. Latency can be calculated by measuring the time it takes for a data packet to travel from its source to its destination and back again. This measurement is known as round-trip time (RTT) and is typically measured in milliseconds.
To calculate RTT, you simply send a packet from the source device to the destination device and measure the amount of time it takes for that packet to return. You can repeat this process multiple times and take an average of the results for a more accurate measurement.
Jitter, on the other hand, is calculated by measuring the variation in latency over time. To calculate jitter, you first need to measure latency as described above. Then, you need to compare each successive RTT measurement with the previous one. The difference between these measurements represents jitter.
It’s important to note that there are tools available that can automate these calculations for you, such as network monitoring software or online speed tests. These tools provide easy-to-understand metrics like ping time (latency) and upload/download speeds (throughput), making it simple to track changes in network performance over time.
By regularly monitoring your network’s latency and jitter levels, you can identify potential issues before they become major problems – helping ensure smooth operations across all areas of your business or personal life where connectivity matters most!
featured Image by – Mika Baumeister on Unsplash








