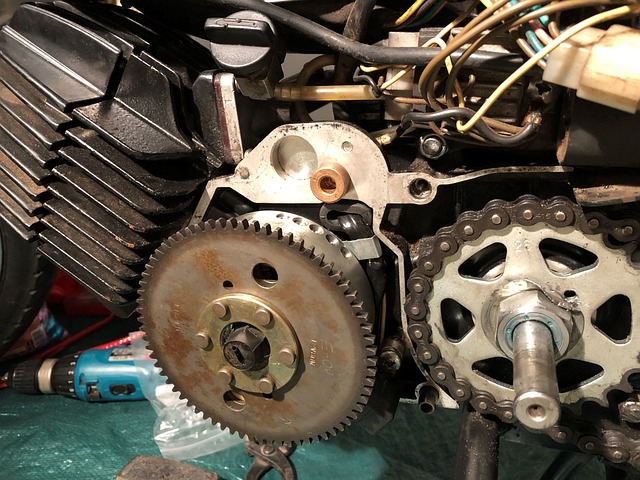
A flywheel is used to store rotational energy, while a flexplate helps transfer engine torque from the crankshaft to the transmission. Flywheels also have higher mass than flexplates which helps them act as dampeners for vibrations caused by engines.
What is a flywheel?
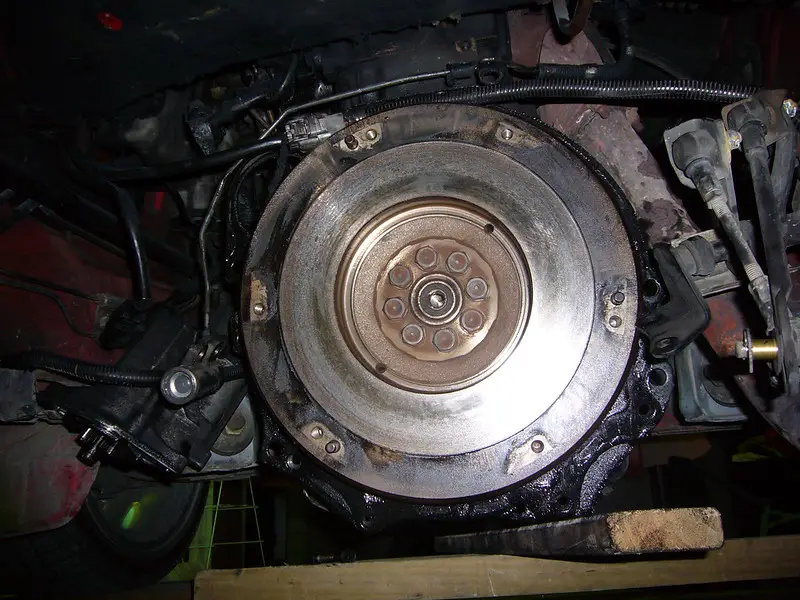

When it comes to automotive engines, a flywheel is a circular disc with teeth on the edge that meshes with the starter motor. The main purpose of a flywheel is to keep the engine crankshaft spinning so that it can start the engine and maintain momentum once it’s running.
What is a flexplate?
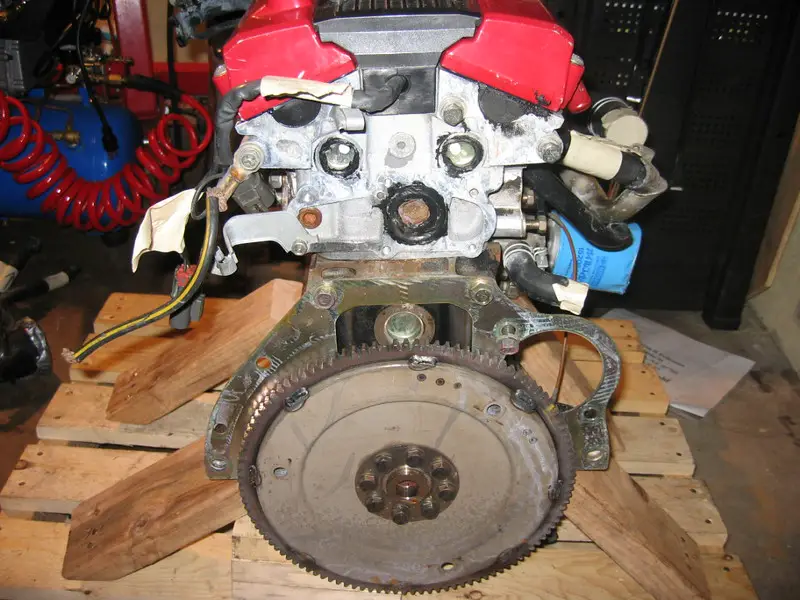

A flexplate is a type of flywheel that is commonly used in vehicles with automatic transmissions. The flexplate is attached to the crankshaft and has a series of teeth or splines that mesh with the transmission’s torque converter. The flexplate’s function is to transfer power from the engine to the transmission.
The difference between flywheel and flexplate
The main difference between a flywheel and a flexplate is that a flywheel is made of steel and is bolted to the crankshaft while a flexplate is usually made of aluminum and welded to the torque converter. A flywheel weighs more than a flexplate because it needs to be heavy enough to keep the engine from stalling when the clutch is disengaged. A flexplate does not need to be as heavy because it is not connected directly to the engine.
How to choose the right one for your car
There are a few things to consider when choosing the right flywheel or flexplate for your car. The first is the weight of the flywheel or flexplate. The heavier the flywheel or flexplate, the more inertia it will have and the more engine power it can transfer. This can be beneficial for drag racing applications where large amounts of torque are required. However, a lighter flywheel or flexplate will be easier to rev and can provide better acceleration.
Another consideration is the material that the flywheel or flexplate is made from. Steel is the most common material, but aluminum or even carbon fiber can be used in some applications. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of strength, weight, and cost.
Finally, you’ll need to choose a flywheel or flexplate with the correct bolt pattern for your car’s crankshaft. Most aftermarket units use a universal bolt pattern, but it’s still important to double-check before making your purchase.
With all of these factors in mind, you should be able to choose the right flywheel or flexplate for your car. If you’re still unsure, consult with a knowledgeable automotive specialist who can help you select the best option for your application.
The advantages and disadvantages of a flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device that stores rotational energy by spinning a heavy disc or wheel, and can be used for various applications, including energy storage and power backup. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of using a flywheel:
Advantages:
- High energy density: Flywheels have a high energy density, meaning they can store a significant amount of energy in a small amount of space. This makes them a good option for applications where space is limited.
- Long lifespan: Flywheels have a long lifespan, typically lasting for decades with minimal maintenance. This makes them a cost-effective option for long-term energy storage.
- Quick response time: Flywheels can respond quickly to changes in demand, making them useful for applications that require rapid power delivery or backup.
- No emissions: Flywheels do not produce any emissions, making them a clean and environmentally-friendly option for energy storage.
Disadvantages:
- Limited energy storage: Flywheels have a limited energy storage capacity compared to other energy storage technologies, such as batteries or pumped hydro storage. This can limit their usefulness for some applications.
- High cost: Flywheels can be expensive to manufacture and install, particularly for larger systems. This can make them a less cost-effective option for some applications.
- Mechanical complexity: Flywheels require precise mechanical components and control systems to function properly, which can add to the cost and complexity of the system.
- Safety concerns: Flywheels operate at high speeds and can be dangerous if not properly designed and maintained. This requires careful attention to safety protocols and regular maintenance to ensure safe operation.
Flywheels offer some unique advantages for energy storage and power backup, such as high energy density, long lifespan, and quick response time. However, their limited energy storage capacity, high cost, mechanical complexity, and safety concerns may make them less suitable for some applications.
The advantages and disadvantages of a flexplate
A flexplate is a circular plate that connects the engine to the torque converter in an automatic transmission vehicle, and is used to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of using a flexplate:
Advantages:
- Lightweight: Flexplates are typically made of lightweight materials, such as aluminum or high-strength steel, which can reduce the overall weight of the vehicle and improve fuel efficiency.
- Durable: Flexplates are designed to withstand high levels of torque and can last for many years with proper maintenance.
- Efficient power transfer: Flexplates are designed to transfer power from the engine to the transmission efficiently, which can help improve the performance of the vehicle.
- Less vibration: Flexplates are designed to reduce vibration and harshness during operation, which can improve the overall ride quality of the vehicle.
Disadvantages:
- Limited torque capacity: Flexplates have a limited torque capacity compared to other types of torque converters, which can limit their use in high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
- Susceptible to damage: Flexplates can be damaged if they are not installed properly or if they are subjected to excessive torque or stress. This can result in costly repairs or replacement.
- Less responsive than manual transmissions: Automatic transmissions, which use a flexplate, are typically less responsive than manual transmissions, which can limit their use in high-performance driving applications.
- More complex: Automatic transmissions, which use a flexplate, are more complex than manual transmissions and can require more maintenance and repairs over time.
Flexplates offer some unique advantages for automatic transmission vehicles, such as lightweight construction, durability, efficient power transfer, and reduced vibration. However, their limited torque capacity, susceptibility to damage, and reduced responsiveness may make them less suitable for high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
What is the function of flexplate?
A flexplate is a circular plate that is attached to the crankshaft of an engine. It has a series of teeth that mesh with the starter ring gear to spin the engine during starting. Once the engine is running, the flexplate also serves as a support for the torque converter.
What is the purpose of a flywheel?
The purpose of a flywheel is to keep the engine crankshaft from turning when the engine is not running. The flywheel is attached to the back of the engine and has a large, heavy ring that goes around the outside of it. The ring is connected to the crankshaft and spins with it. When the engine is not running, the flywheel keeps the crankshaft from turning.
What happens if there is no flywheel and flexplate?
If there is no flywheel, the engine will not run. The starter motor will not be able to engage the engine and the engine will not be able to turn over. This is because the starter motor needs something to grip onto in order to turn the engine over and without a flywheel, there is nothing for it to grip onto.
If there is no flexplate, the engine will not be able to turn over. The pistons will not be able to move up and down, and the crankshaft will not be able to rotate. This will cause the engine to stall.
What causes a flywheel to fail?
There are a few reasons that can cause a flywheel to fail. The most common reason is due to an imbalance in the wheel. This can happen over time as the wheel wears down, or if it was not properly balanced when it was initially manufactured. Another reason for failure is cracks or breaks in the wheel itself. This can be caused by excessive heat, such as from racing engines, or simply from age and wear and tear. Finally, the bolts that hold the flywheel onto the engine can come loose, causing the flywheel to spin independently of the engine. If this happens, it will quickly destroy the flywheel.