There are four main types of animals: herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and detritivores. Each type of animal has a different diet and different way of getting food. Herbivores are animals that only eat plants. Carnivores are animals that only eat other animals. Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and other animals. Detritivores are animals that eat dead plant or animal matter.
Herbivores
Herbivores are animals that consume plants. They are typically found in nature, grazing on grasses and other vegetation. Some common examples of herbivores include deer, rabbits, and elephants.
Carnivores
Carnivores are animals that consume other animals. They typically have sharp teeth and claws that help them kill and eat their prey. Some common examples of carnivores include lions, tigers, and bears.
Omnivores
Omnivores are animals that consume both plants and animals. They are adaptable creatures that can find food sources in a variety of different habitats. Some common examples of omnivores include humans, pigs, and raccoons.
Detritivores
Detritivores are animals that consume dead organic matter. They play an important role in the ecosystem by breaking down rotting vegetation and returning nutrients to the soil. Some common examples of detritivores include worms, ants, and termites.
Key differences difference between herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and detritivores
Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores are all types of animals classified based on their feeding habits. Here are the key differences between them:
Herbivores: Herbivores are animals that mainly eat plants, leaves, fruits, seeds, and flowers. They have long digestive tracts and special digestive enzymes that help them break down plant cellulose. Examples of herbivores include cows, horses, rabbits, and deer.
Carnivores: Carnivores are animals that mainly eat other animals. They have sharp teeth and powerful jaws that help them hunt and kill prey. Examples of carnivores include lions, tigers, wolves, and eagles.
Omnivores: Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. They have a combination of sharp and flat teeth that allow them to eat a variety of foods. Examples of omnivores include humans, bears, pigs, and raccoons.
Detritivores: Detritivores are animals that feed on dead and decaying plant and animal matter, such as fallen leaves, dead animals, and feces. They help to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. Examples of detritivores include earthworms, millipedes, and some species of beetles.
The main difference between these types of animals is their primary source of food, which is reflected in their physical adaptations and digestive systems.
What are the 4 levels of the food chain?
The food chain is the sequence of who eats whom in the wild. There are four main levels of the food chain: producers, consumers, decomposers, and detritivores.
- Producers are plants or other organisms that make their own food from sunlight and nutrients in the soil. They are at the bottom of the food chain because they provide food for everything else.
- Consumers are animals that eat other organisms for food. They can be divided into two groups: herbivores and carnivores. Herbivores are animals that only eat plants, while carnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals.
- Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms into simpler substances that can be used by producers to make new organic matter. Without decomposers, there would be a lot of waste material accumulating on the earth’s surface.
- Detritivores are animals that eat decomposing organic matter (detritus). They help to recycles nutrients back into the soil so that producers can use them to make new organic matter.
Examples for Herbivores
(Photo by Scott Carroll on Unsplash )
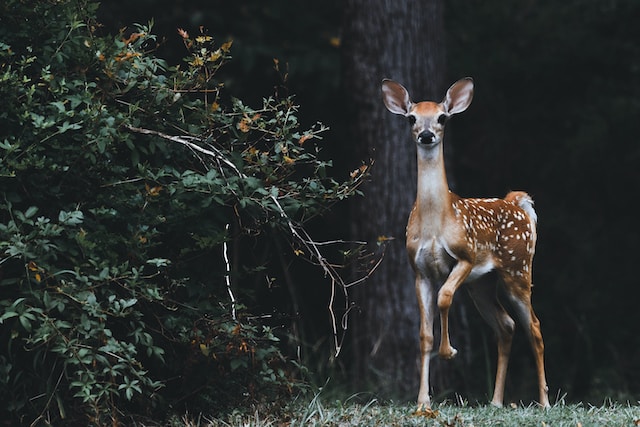

There are many different types of herbivores, but some examples include: deer, rabbits, koalas, and elephants. These animals all have different ways of obtaining their food, but they all primarily eat plants.
Deer are perhaps the most well-known type of herbivore. They live in wooded areas and eat leaves, grasses, and other vegetation. Rabbits are another common type of herbivore. They live in burrows and eat a variety of plants, including vegetables.
Koalas are another type of herbivore that is often misunderstood. Koalas are actually marsupials, which means they carry their young in a pouch. Koalas primarily eat eucalyptus leaves, but they will also eat other types of foliage if necessary.
finally, elephants are the largest type of herbivore. They live in Africa and Asia and eat a variety of plants, including grasses, tree bark, and fruits.
Examples for Carnivores
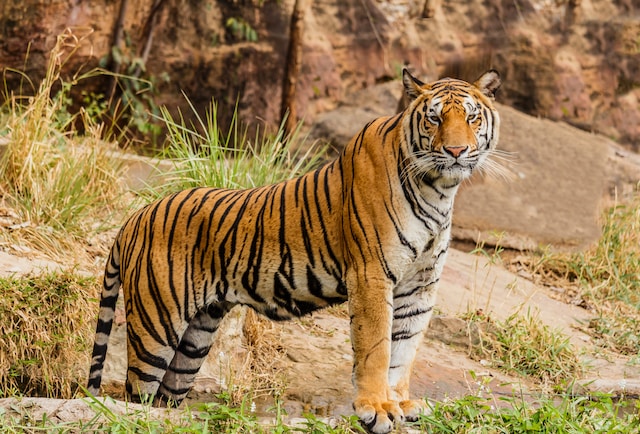

Carnivores are animals that primarily feed on other animals. Here are some examples of carnivores:
Lions: Lions are large, powerful predators that are often referred to as the “king of the jungle.” They hunt and feed on a variety of prey, including antelopes, zebras, and wildebeest.
Tigers: Tigers are the largest of the big cats and are known for their distinctive striped coats. They hunt and feed on a variety of prey, including deer, wild pigs, and buffalo.
Wolves: Wolves are highly social animals that hunt and feed on a variety of prey, including deer, elk, and moose. They are also known to scavenge on carrion when food is scarce.
Eagles: Eagles are birds of prey that feed on a variety of animals, including fish, rabbits, and small mammals. They are known for their sharp talons and beaks, which they use to catch and kill their prey.
Sharks: Sharks are a diverse group of carnivorous fish that inhabit oceans around the world. They feed on a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and seals.
Carnivores come in many different shapes and sizes, but they all share the common characteristic of being predators that rely on other animals as their primary source of food.
Examples for Omnivores
(Photo by Ahmed Fahmi on Unsplash )
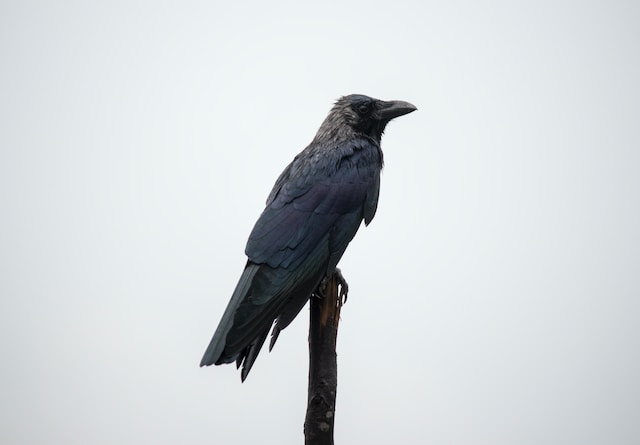

Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. Here are some examples of omnivores:
Humans: Humans are omnivores, and we consume a wide variety of foods from both plant and animal sources. Our diets include fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, dairy, and more.
Bears: Many species of bears are omnivores, and they feed on a variety of foods depending on their geographic location and the time of year. Some common foods for bears include berries, nuts, fish, and small mammals.
Pigs: Pigs are omnivores and will eat almost anything, including plants, insects, and small animals. In agriculture, pigs are often fed a diet that includes grains, soybeans, and other plant-based foods.
Raccoons: Raccoons are omnivorous mammals that are found throughout North and Central America. They feed on a variety of foods, including fruits, insects, small animals, and human garbage.
Crows: Crows are omnivorous birds that are found throughout the world. They feed on a variety of foods, including insects, fruits, seeds, and small animals.
Omnivores are highly adaptable animals that can survive in a wide variety of habitats and feed on a diverse range of foods.
Examples for Detritivores
(Photo by Nick Kwan on Unsplash )
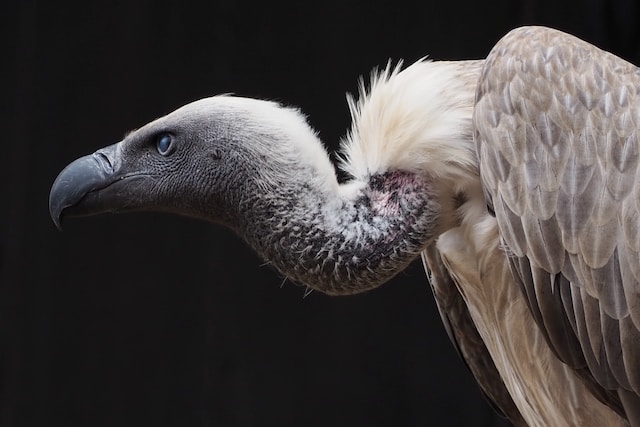

Detritivores are animals that feed on dead and decaying plant and animal matter. Here are some examples of detritivores:
Earthworms: Earthworms are commonly found in soil and are known for their ability to break down organic matter. They feed on dead plant material and other organic matter, and their activity helps to improve soil structure and fertility.
Millipedes: Millipedes are a type of arthropod that feed on decaying leaves and other plant matter. They help to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Beetles: Some species of beetles are detritivores and feed on dead plant and animal matter. They play an important role in breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil.
Vultures: Vultures are birds of prey that feed on the carcasses of dead animals. They help to clean up the environment by consuming animal remains that might otherwise accumulate.
Maggots: Maggots are the larvae of flies and are often found in decaying organic matter, such as rotting meat or animal feces. They help to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Detritivores play an important role in breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients to the ecosystem. Without detritivores, organic matter would accumulate and nutrients would become locked up, leading to a less healthy and productive ecosystem.
Featured Image By – monica_aulich from Pixabay