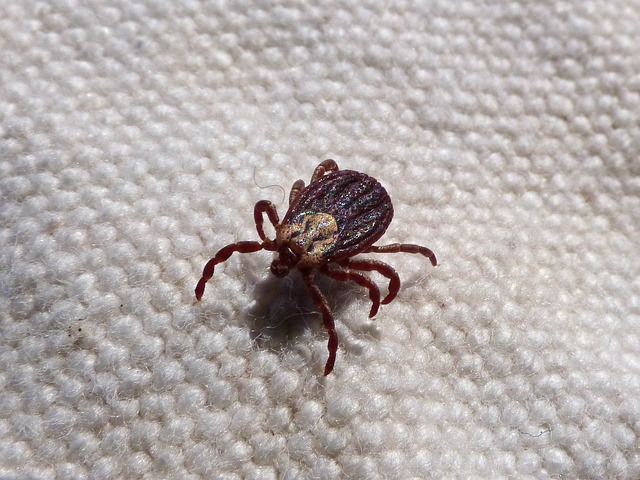
Ticks can transmit several diseases to humans and animals, which makes them more dangerous than fleas. Fleas, on the other hand, are less of a health risk but cause discomfort to both humans and pets alike.
Ticks
(Photo by Erik Karits on Unsplash )
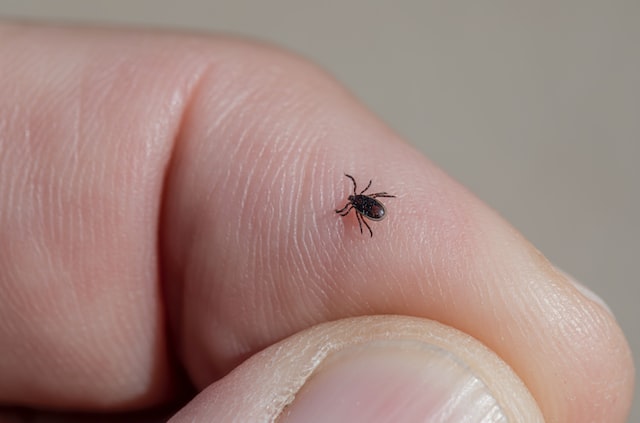

Ticks are parasitic arachnids that feed on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. They are usually found in wooded or brushy areas, and can attach themselves to their hosts by crawling or climbing onto them. Ticks can transmit diseases to their hosts, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and tularemia.
Fleas
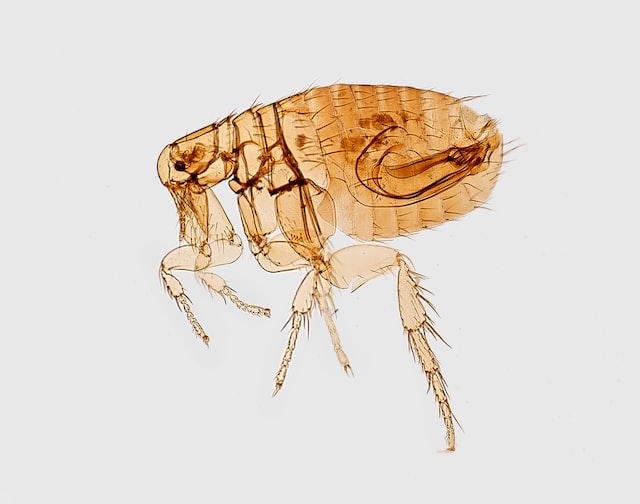
There are many differences between ticks and fleas, but the most notable difference is that fleas are wingless while ticks have four wings. Fleas are also much smaller than ticks; an adult flea is about the size of a pen tip while an adult tick can be as large as a grape. Ticks can be either hard or soft bodied, but all fleas have hard bodies.
Fleas are blood-sucking parasites that feeds on the blood of mammals and birds. They are especially attracted to warm-blooded animals, which is why they are often found on dogs and cats. Fleas can jump great distances – up to 200 times their own body length – so they can quickly spread from one animal to another. Fleas can also live for several months without feeding, so they can survive in even the cleanest of homes.
The difference between ticks and fleas?
Ticks and fleas are both small, wingless insects that feed on the blood of animals. Fleas are normally black or brown, while ticks can be various colors depending on their species. Ticks are bigger than fleas, with some adult ticks being as large as a pea. Both insects have mouthparts that pierce the skin and suck blood.
There are several key differences between ticks and fleas. Ticks are vectors for disease, meaning they can transmit diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever to humans and animals. Fleas do not carry diseases and are not known to transmit any diseases to humans or animals. Ticks attach themselves to their host and can stay attached for days or even weeks, while fleas only feed for a few minutes before falling off their host. Finally, ticks go through multiple life stages (egg, larva, nymph, adult), while fleas only have two stages (egg and adult).
How to identify ticks from fleas?
Ticks and fleas are both small, parasites that feed off the blood of their host. Both can transmit diseases to their hosts, and both can be a nuisance. So, how can you tell them apart?
Ticks are generally larger than fleas, and their bodies are more elongated. They have small mouths that they use to pierce the skin of their host and then suck out blood. Ticks can be different colors depending on their species, but they are typically dark brown or reddish brown.
Fleas are smaller than ticks and have narrower bodies. Their mouths are designed for piercing skin and sucking out blood, but they also have two large claws that they use to help them move around. Fleas are usually dark brown or black in color.
If you find a small, dark-colored parasite on your pet or yourself, it is likely a flea or a tick. If you are unsure, you can always consult a veterinarian or pest control specialist for assistance.
How to prevent ticks and fleas
To prevent ticks and fleas, there are a few things you can do. First, make sure your pets are up to date on their vaccinations. This will help to keep them from getting sick if they do come in contact with ticks or fleas. Secondly, keep your yard clean and free of debris. This will make it less likely for ticks and fleas to take up residence there. Finally, use tick and flea repellent whenever you go outside, especially during the warm months when these pests are most active.
How to remove a tick
If you find a tick on your body, it’s important to remove it as soon as possible. The best way to remove a tick is to use a pair of tweezers to grip the tick by the head, as close to the skin as possible. Gently pull the tick straight out from the skin. Avoid crushing the tick’s body, which could release harmful bacteria into your bloodstream.
Once the tick is removed, clean the area with soap and water or an alcohol-based disinfectant. You should also wash your hands thoroughly after coming into contact with a tick.
How to remove a flea
Removing a flea can be a little tricky, but here are some steps you can follow:
- Wear protective gloves: Fleas can carry diseases and can bite, so it’s important to wear gloves to protect yourself.
- Use a flea comb: A flea comb has fine teeth that can help you remove fleas from your pet’s fur. Make sure you have a bowl of soapy water nearby to dunk the comb in and drown any fleas you remove.
- Apply a flea treatment: There are many flea treatments available for pets, such as topical treatments or oral medications. Talk to your veterinarian to determine which treatment is best for your pet.
- Wash bedding and vacuum: Fleas can hide in bedding, carpets, and furniture, so it’s important to wash your pet’s bedding and vacuum your home regularly to remove any fleas and eggs.
- Seek professional help: If your flea problem persists or is particularly severe, it may be necessary to seek professional help from a pest control expert.
Remember, prevention is the best way to avoid flea infestations. Regularly grooming and treating your pets, washing bedding and vacuuming, and maintaining a clean home environment can help prevent fleas from taking hold in the first place.
Can ticks live on humans?
Ticks can live on humans, but they are not able to reproduce on humans. Ticks typically attach themselves to a human in order to get a blood meal. Ticks can transmit diseases to humans through their bites, so it is important to be aware of the risks associated with ticks and take steps to avoid being bitten.
The dangers of fleas
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that are blood-sucking parasites of mammals and birds. They can be found in nearly every corner of the world and their bites can transmit a number of serious diseases to both humans and animals.
Flea bites are not only painful, they can also lead to a number of health problems including skin irritation, allergies, anemia, and even death in young children or animals. Fleas can also transmit diseases like typhus and plague. In fact, fleas were responsible for the spread of the Black Death during the 14th century which killed millions of people across Europe.
While most flea species prefer to feed on animal blood, some will bite humans if given the opportunity. To avoid being bitten by fleas, it’s important to take measures to prevent them from entering your home in the first place. This includes regular vacuuming and laundering of bedding, as well as using insecticide sprays or powders around the perimeter of your home.
The dangers of ticks
Ticks are small blood-sucking parasites that can be found in woods and fields across the country. They attach themselves to their victims, usually animals such as deer or rodents, and feed on their blood. Ticks can also infect humans with diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and tularemia.
Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne disease in the United States, and it can be debilitating if not treated properly. Symptoms of Lyme disease include fever, headaches, fatigue, and a bulls-eye rash. If left untreated, Lyme disease can cause joint pain, neurological problems, and even death.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is another tick-borne disease that can be deadly if not treated promptly. Symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever include high fever, severe headache, muscle pain, nausea and vomiting. This disease can lead to serious health complications such as seizures and paralysis if it is not treated immediately.
Tularemia is a rare but potentially fatal tick-borne illness that affects both animals and humans. Symptoms of tularemia include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches and pneumonia. If left untreated tularemia can lead to organ failure and death.
Featured Image By – Image by Marc Pascual from Pixabay








